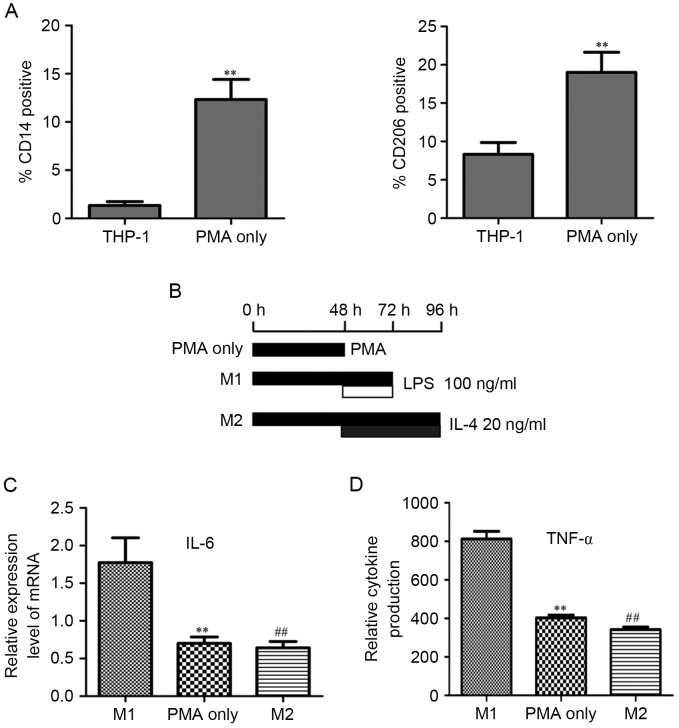
Figure 1.
PMA treatment differentiates THP-1 cells to M2 macrophages. (A) THP-1 cells treated with 320 nM PMA for 48 h exhibited significant induction for CD14 (marker for macrophage differentiation) and CD206 (marker for M2 macrophages differentiation). **P<0.01. (B) After treatment with 320 nM PMA for 48 h, THP-1 cells differentiated to the ‘PMA-treated THP-1 macrophages’ (labeled ‘PMA only’). ‘M1-polarized THP-1 macrophages’ (M1) were obtained by treating THP-1 cells with PMA for 72 h and polarizing them with Th1 cytokine (100 ng ml−1 LPS) for 24 h (added 48 h after PMA). For the ‘M2-polarized THP-1 macrophages’ (M2), THP-1 cells were treated with PMA for 48 h, then cultured with PMA plus 20 ng ml−1 IL-4 for another 48 h. (C) PMA-treated THP-1 macrophages (PMA only) and M2-polarized THP-1 macrophages (M2) both had significantly lower mRNA level of IL-6, compared with that of M1-polarized THP-1 macrophages (M1). (D) PMA-treated THP-1 macrophages (PMA only) and M2-polarized THP-1 macrophages (M2) both had significantly lower cytokine level of TNF-α compared with that of M1-polarized THP-1 macrophages (M1). All P<0.01; ** PMA only vs. M1; ## M2 vs. M1. TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.