FIGURE 4.
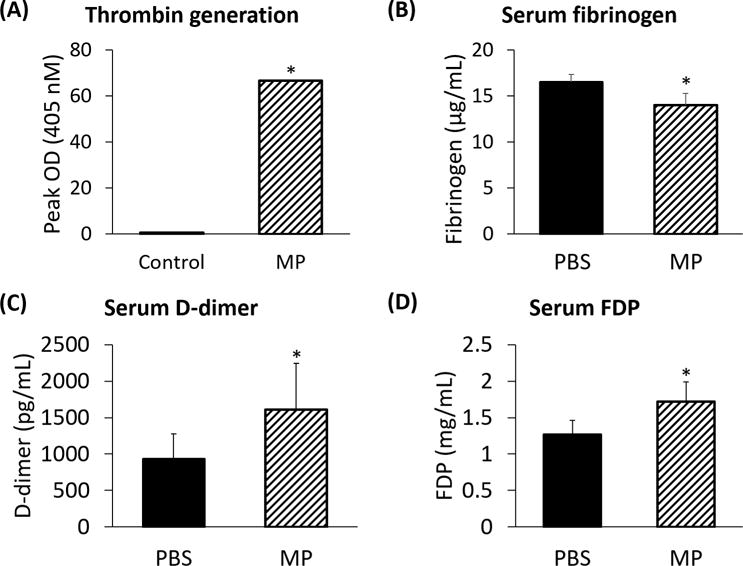
(A) Erythrocyte-derived microparticles demonstrate a nearly hundredfold greater conversion of prothrombin to thrombin than controls (66.60±0.03 vs 0.70±0.01 peak OD; p<0.05). Transfusion of microparticles from pRBC units causes a decrease in (B) circulating fibrinogen levels (16.5 vs 14.0 μg/mL), (C) D-dimer levels (0.9±0.3 vs 1.6±0.6 ng/mL), and (D) fibrin degradation product levels (1.3±0.2 vs 1.7±0.3 mg/mL) as compared with control (each p<0.05).
