Table 1.
Fatty acylation and prenylation of proteins.
| Modification | Lipid | Amino acid modified | Linkage | Representative proteins | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-acylation | C16:0 Palmitic acid |
Cysteine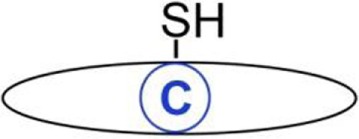
|
Thioester | IFITM3, toll-like receptor 2, hemagglutinin (HA), glycoprotein G of vesicular stomatitis virus, Lyn, and other Src kinases | (8–12) |
| C18:0 Stearic acid |
HA and transferrin receptor | (9, 13) | |||
| C16:1 Palmitoleic acid |
IFITM3 | (14) | |||
| C18:1 Oleic acid |
H-Ras | (14, 15) | |||
| C20:4 Arachidonic acid |
Fyn kinase | (15) | |||
| N-acylation | C14:0 Myristic acida |
Glycine
|
Amide | Gag of human immunodeficiency virus-1, Lck, and other Src kinases, Arf1 | (16–19) |
| C16:0 Palmitic acid |
Gαs | (20) | |||
| C16:0 Palmitic acid |
Cysteine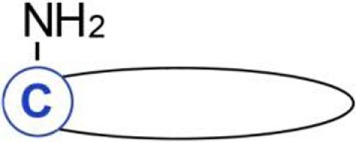
|
Amide | Sonic hedgehogb | (21) | |
| ε-N-acylation | C14:0 Myristic acid |
Lysine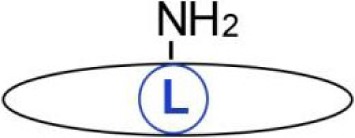
|
Amide | Tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin-1, and α-hemolysin of Escherichia coli | (22, 23) |
| C16:0 Palmitic acid |
Adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis | (24) | |||
| O-acylation | C16:0 Palmitic acid |
Serine or threonine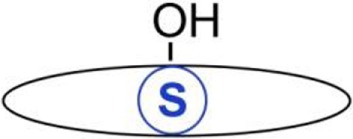
|
Oxyester | Histone H4 | (25) |
| C8:0 Octanoic acid |
Ghrelin | (26) | |||
| C16:1 Palmitoleic acid |
Wnt proteins, e.g., Wnt3ac | (27) | |||
| S-prenylation | Farnesyl | Cysteine
|
Thioether | H- and N-Ras | (28) |
| Geranylgeranyl | Rab proteins | (28) | |||
Attachment of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor or phosphatidylethanolamine (29) to the C-terminus of proteins is also a form of lipidation but is not shown here.
aN-myristoylation is in most cases co-translational, but during apoptosis caspases can cleave some proteins, such as BID, exposing their N-terminal glycine residue, which is then modified by attachment of myristate (30).
bHedgehog proteins are additionally modified by covalent attachment of cholesterol to their C-terminus (31).
cO-acylation of Wnt proteins is reversed by Notum of the α/β hydrolase superfamily (31).
