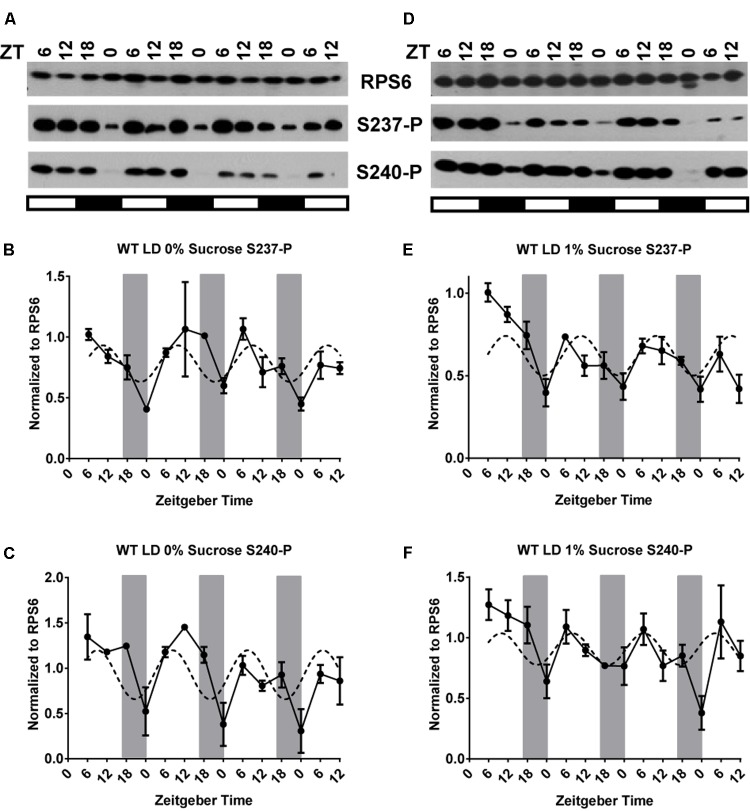
FIGURE 1.
In wild-type seedlings under a light dark cycle, light-driven and clock-driven cycles combine into a low-amplitude cycle with peak phosphorylation during the day. Seedlings of wild-type Arabidopsis were entrained in a light-dark cycle for 12 days, then grown under the same conditions for another three and a half days and scored for phosphorylation of RPS6 (ribosomal protein eS6) every 6 h. Seedlings were grown on medium lacking sucrose (A–C) or containing 1% sucrose (D–F). Phosphorylation at S237 (S237-P) and at S240 (S240-P) was quantified using phosphospecific antibodies. (A,D) Representative immunoblots for S237-P and S240-P. The total amount of RPS6 was determined with an antibody against an amino-terminal peptide of RPS6. Time is given in hours of zeitgeber time (ZT) after lights-on on Day 12. The white and black bars indicate light and dark conditions, respectively. (B,C,E,F) Immunoblot signals for S237-P and S240-P were quantified using ImageJ software and normalized against total RPS6 signals from the same time point. Each data series was median-centered and data from multiple replicates were averaged. Error bars show the standard error of the mean from n = 2 replicates for 0% sucrose and n = 3 for 1% sucrose, grown at different times, which were immunoblotted once or twice each. A sine curve was fitted to the data as described in Section “Materials and Methods” (dashed line). The dark gray bars indicate the daily dark period.