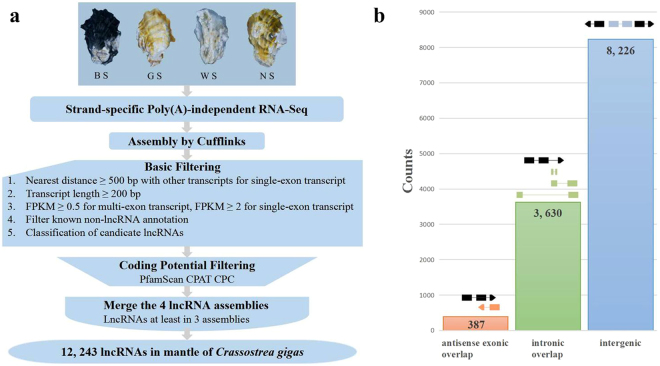
Figure 1.
Identification and classification of Crassostrea gigas lncRNAs. (a) Overview of the computational filtering pipeline used for the identification of oyster lncRNAs. See main text and Materials and Methods for details. Ellipse box highlights the final number of transcripts that passed all filters and were considered high-confidence oyster lncRNAs. (b) Number of lncRNAs in each of the three main classes defined by their genomic location relative to protein-coding genes. A schematic representation of lncRNAs (colour) position relative to protein-coding genes (black) is shown on the top. lncRNAs with “antisense exonic overlap” (red) have at least one exon that overlaps with an exon of a protein-coding gene on the opposite strand. lncRNAs with “intronic overlap” (green) are defined as transcripts that have overlap with another protein-coding gene but no exon–exon overlap (no overlap with exons of the overlapping genes). “Intergenic” lncRNAs (blue) have no overlap with any protein-coding gene.