Fig. 2.
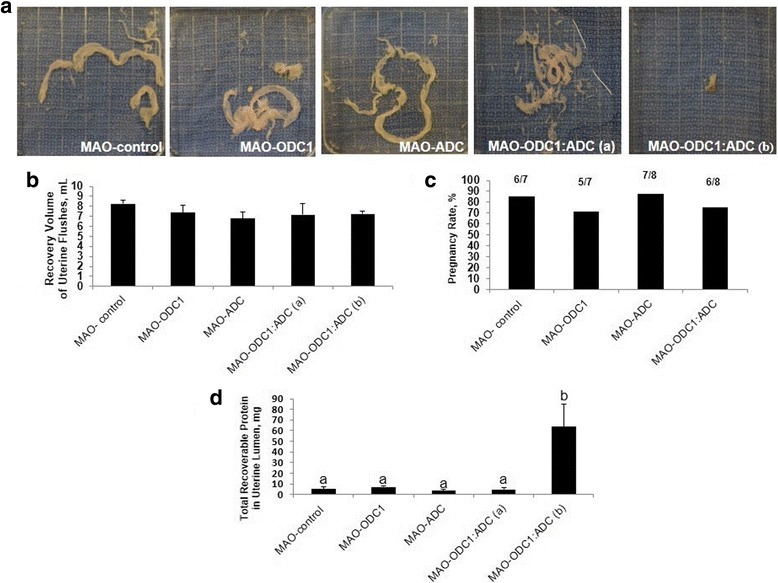
Gross morphology of ovine conceptuses on d 16 of pregnancy following knockdown of translation of mRNAs for ODC1, ADC and their combination (ODC1:ADC). [a] Compared to MAO-control conceptuses (Panel A1; n = 6), in vivo knockdown of translation of mRNAs for ODC1-MAO (Panel A2, n = 5) and ADC-MAO (Panel A3, n = 7) did not adversely affect development of the conceptuses. However, the combination knockdown of translation of both ODC1 and ADC (MAO-ODC1: MAO-ADC) resulted in two phenotype based on their morphological and functional development. The MAO-ODC1:MAO-ADC (a) conceptus phenotype (Panel A4, n = 2) was normal, healthy and elongated, while the MAO-ODC1:MAO-ADC (b) conceptus phenotype (Panel A5, n = 4) was abnormal, fragmented and not elongated. [a] Recovery volume of uterine flushes [b] and pregnancy rate [c] were not different (P > 0.05) among treatment groups. However total recoverable protein in uterine flushes from MAO-ODC1: MAO-ADC (b) was greater (P < 0.05) from values for the other treatment groups [d]. Means with different superscript letters were different (P < 0.05). Data are presented as means and SEM
