Figure 2.
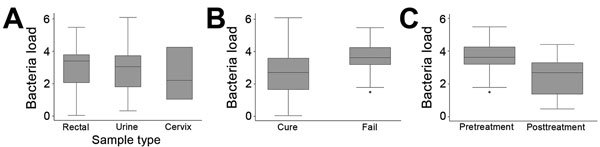
Mycoplasma genitalium bacterial loads (log10) and treatment outcomes, Melbourne Sexual Health Centre, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 2012–2016. A) M. genitalium load compared in urine (n = 67), rectal swab (n = 26), and cervical swab (n = 3) samples. For urine vs. rectal samples, p = 0.56; for urine vs. cervical samples, p = 0.70. B) Comparison of pretreatment M. genitalium loads in infections not cured (n = 26) and cured (n = 71) by pristinamycin. p<0.01. C) Comparison of M. genitalium loads in pretreatment and posttreatment samples from cases in which pristinamycin failed (n = 26). p<0.001..Box plots indicate 25th percentile (bottom of box), 75th percentile (top of box), median (horizontal line within box), and range (whiskers). Dots represent outlying individual observations.Dots under the error bars indicate individual outliers.
