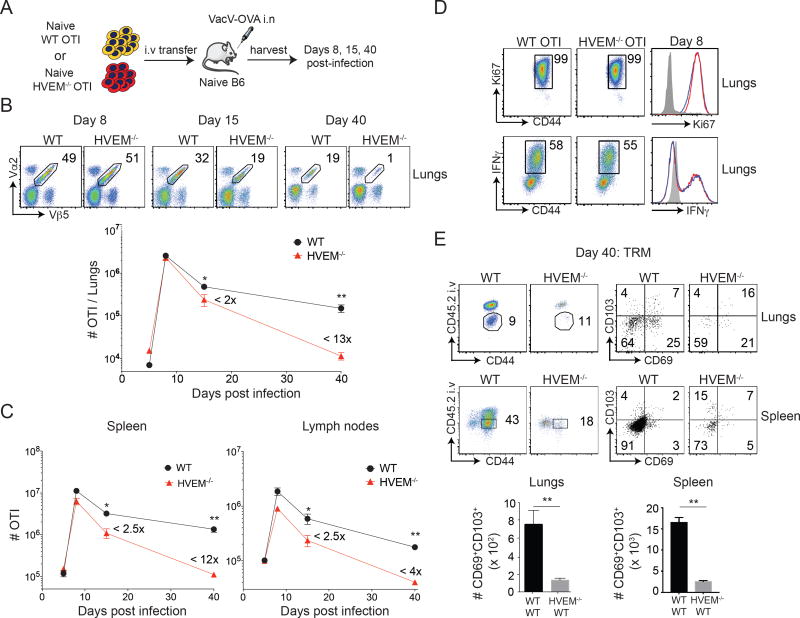
Figure 1. HVEM on CD8 T cells is required for memory generation after respiratory vaccinia virus infection.
(A) Equal numbers (5 × 104) of WT and HVEM−/− naïve (CD44lo) OT-I (Vα2+Vβ5+) transgenic CD8 T cells were adoptively transferred into BL/6 mice and infected with rVacV-WR-OVA (2 × 104 PFU i.n) the following day. (B) Lungs, (C) spleen and lymph nodes were harvested at days 6, 8, 15 and 40 post-infection and stained for CD8, CD44, Vα2, and Vβ5 and frequencies of OT-I CD8 T cells determined. (D) OT-I cells from lungs of recipient mice at day 8 were stained for Ki67 intranuclearly and restimulated in vitro with OVA and stained for IFN-γ. (E) At day 40 post-infection, recipient mice were injected with anti-CD45.2 antibody intravenously, three minutes before euthanizing. Representative plots of CD45.2 and CD44 were pre-gated on CD8+OT-I (Vα2+Vβ5+) cells. The gated CD45.2 negative cells were analyzed for the expression of CD103 and CD69 using flow cytometry and total numbers of cells calculated in lungs and spleen. *, P<0.05; **, p<0.01 and results are the mean ± SEM (n = 3 mice/group). Similar results were obtained in four independent experiments.