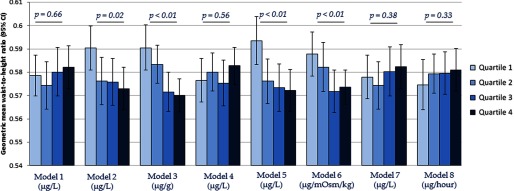
Figure 4.
Geometric mean (95% CI) of waist-to-height ratio across estimated urinary arsenic 1a quartiles by urine dilution adjustment approaches. a Estimated as [total arsenic in ] with negative values set to . are for assessment of linear trends across urinary arsenic quartiles. Models refer to: 1) no adjustment for urine dilution; 2) creatinine as an independent covariate in the regression model; 3) arsenic concentration divided by creatinine concentration (); 4) covariate-adjusted standardization of arsenic concentration (); 5) osmolality as an independent covariate in the regression model; 6) arsenic concentration divided by osmolality ( ); 7) urinary flow rate as an independent covariate in the regression model; and 8) arsenic concentration multiplied by urinary flow rate to obtain excretion rate (). All models were additionally adjusted for age (continuous), gender (male/female), race/ethnicity (non-Hispanic white, non-Hispanic black, Mexican American, other Hispanic, or other race/multiracial), and survey cycle (2009–2010 or 2011–2012).