Figure 6.
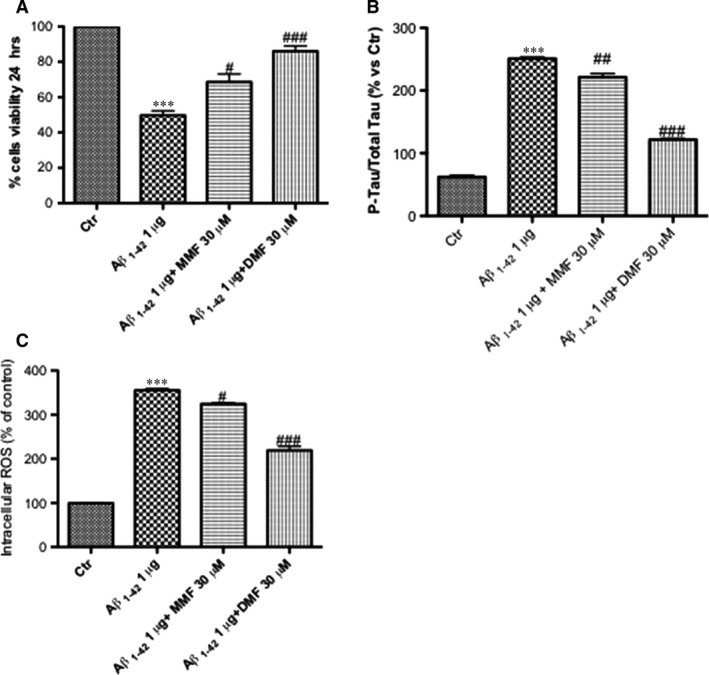
Effect of DMF on viability, p‐tau and ROS production in Aβ1‐42‐treated organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Stimulation of organotypic slides with Aβ1‐42 significantly reduced viability compared to the control group (A). Pre‐treatment with DMF (30 μM), much more than MMF (30 μM), 2 hrs before Aβ1‐42 stimulation, significantly reduced cell death compared to the Aβ1‐42 group (86% versus 68%, respectively) (A). Averages for MTT: 86% DMF versus 49,6% Aβ1‐42; 68,6% MMF versus 49,6% Aβ1‐42. ELISA kit of p‐tau showed an important increase in phosphorylation after Aβ1‐42 stimulation 24 hrs after incubation (B); the pre‐treatment with DMF 30 μM notably reduced the quantity of tau‐phosphorylated protein, more efficiently than MMF 30 μM (B). Averages for p‐Tau‐ELISA kit: 121,6% DMF versus 250,2% Aβ1‐42; 221,4% MMF versus 250,2% Aβ1‐42. Pre‐treatment with MMF 30 μM partially reduced ROS production, while the pre‐treatment with DMF 30 μM has shown a significant reduction in ROS‐produced oxidative stress compared to Aβ1‐42‐stimulated group. (C). Averages for ROS assay: 219,3% DMF versus 355,6% Aβ1‐42; 324,3 MMF versus 355,6% Aβ1‐42. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (A) ***P < 0.001 versus Ctr, ## P < 0,01 versus Aβ1‐42 and ### P < 0.001 versus Aβ1‐42; (B) ***P < 0.001 versus Ctr, ## P < 0.01 versus Aβ1‐42 and ### P < 0.001 versus Aβ1‐42; (C) ***P < 0.001 versus Ctr, ## P < 0,01 versus Aβ1‐42 and ### P < 0.001 versus Aβ1‐42.
