Figure 1.
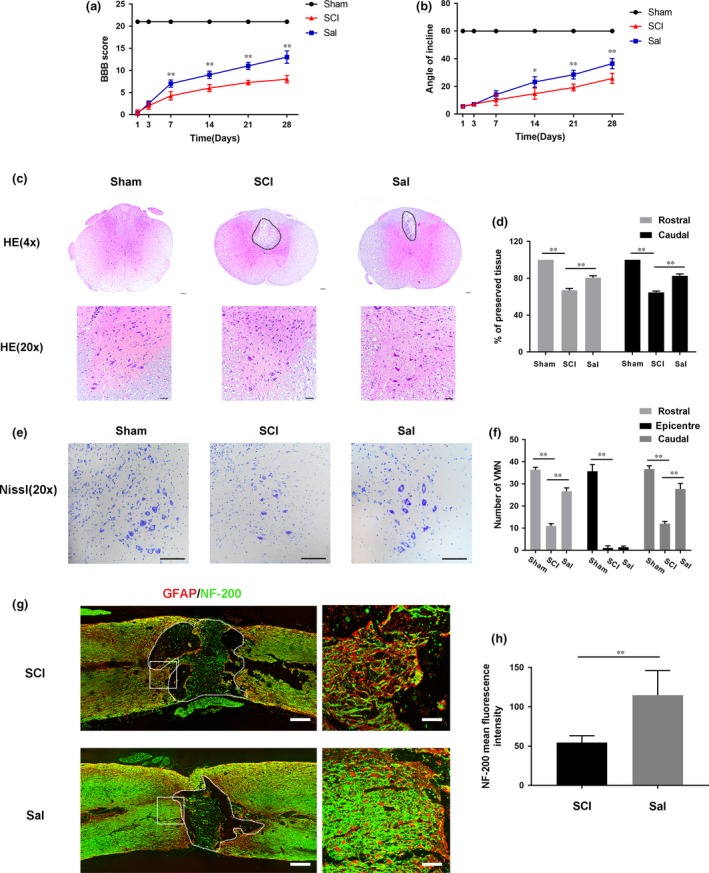
Sal attenuates tissue structural damage, neuron loss and improves functional recovery after experimental acute traumatic SCI (A) Basso, Beattie and Bresnahan (BBB) scores. (B) Inclined plane test scores. (C) H&E stains at 7 days. Scale bars are 100 μm (4×) and 50 μm (20×). Dashed lines area showed cavity of spinal cord. (D) Graphic presentation of the percentage of preserved tissue relative to the transverse area of the spinal cord on the seventh postoperative day. (E) Nissl staining to assess the loss of neurons at 7 days. Scale bars are 50 μm. (F) Counting analysis of VMN at rostral 5 mm, caudal 5 mm and lesion site. (G) Representative images containing neurofilament (NF‐200, green) and GFAP (red) immunofluorescence on spinal cord sections. Dashed lines area showed cavity of spinal cord. Scale bar are = 1000 μm and 50 μm. (H) Quantitative analysis of NF‐200 staining intensity. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D., n = 3 independent experiments. Significant differences between groups are indicated as *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
