Figure 8.
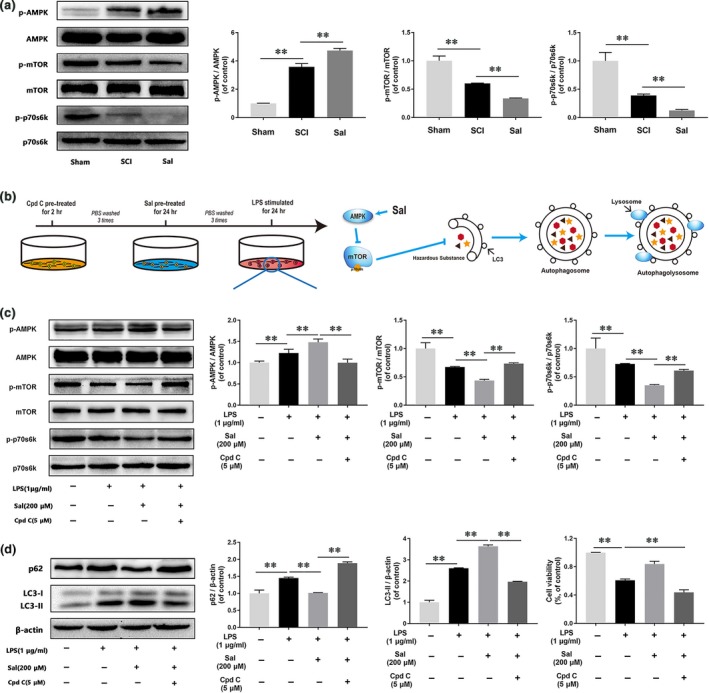
Sal promotes autophagic flux by modulation of AMPK/mTOR pathway in vivo and in vitro (A) Representative Western blots of and quantitative data for p‐AMPK, AMPK, p‐mTOR, mTOR, p‐p70s6k, p70s6k and β‐actin expression in each group rats. The AMPK/mTOR pathway was activated by Sal treatment in the indicated group. (B) Schematic of BV‐2 cell treatments and the relationship between the AMPK/mTOR pathway and autophagic flux. BV‐2 cells were pre‐treated with Cpd C for 2 hrs, followed by washing three times and treatment with Sal for 24 hrs, and then stimulated by LPS for 24 hrs. (C, D) Representative Western blots of and quantitative data for p‐AMPK, AMPK, p‐mTOR, mTOR, p‐p70s6k, p70s6k, p62, LC3 and β‐actin expression in each group of microglia. Sal activated autophagic flux via the AMPK/mTOR pathway, a change that was reversed by compound C. Densitometric analysis of all Western blot bands, whose densities were normalized to those of the corresponding total proteins or β‐actin. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D., n = 3 independent experiments. Significant differences between groups are indicated as *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
