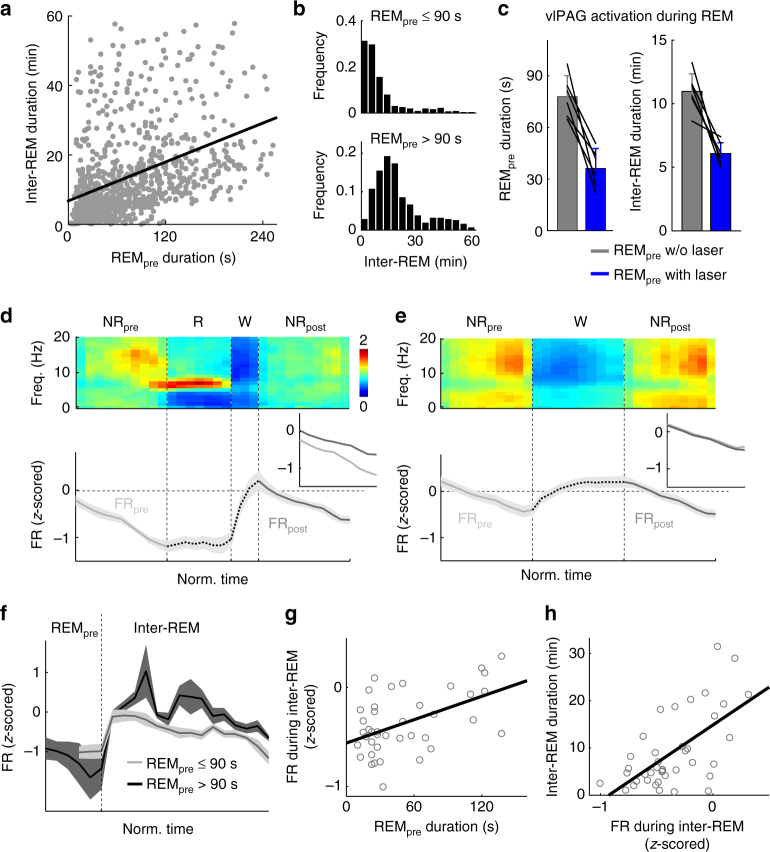
Fig. 6.
Homeostatic modulation of REM sleep and REM-off neuron activity. a Correlation between REM episode duration and subsequent inter-REM interval. Each dot represents a single episode (n = 972 episodes from 27 mice). Line, linear fit (R = 0.39, P = 6.8 × 10−36, T(970) = 13.03). b Distribution of inter-REM interval following short (≤90 s) and long (>90 s) REM episodes. The two distributions are significantly different (P = 2.8 × 10−48, z = −14.60, Wilcoxon rank-sum test). c Effect of closed-loop activation of vlPAG GABAergic neurons on REM sleep duration and subsequent inter-REM interval. Closed-loop stimulation shortened both REM episodes (n = 6 mice, P = 0.002, T(5) = 5.88, paired t-test) and subsequent inter-REM intervals (P = 0.003, T(5) = −5.29). Lines, single mice. Error bar, ±s.d. d Average EEG spectrogram (upper) and mean firing rate (z-scored) of significant REM-off vlPAG GABAergic neurons (lower) during the NREM→REM→wake→NREM transition sequence. Each REM, wake, or NREM episode was temporally normalized. Shading, ±s.e.m. Inset, comparison of firing rates during the NREM episodes preceding (NRpre) and following REM sleep (NRpost). The firing rate during NRpost was higher than that during NRpre (n = 11 units; P = 0.006, T(10) = −3.43, paired t-test). e Similar to d, but for the NREM→wake→NREM sequence. Without the intervening REM episode, the firing rates were similar between NRpre and NRpost (P = 0.42, T(10) = 0.84). f Comparison of vlPAG activity during inter-REM interval following short (≤90 s) and long (>90 s) REM episodes. Following a long REM period, the firing rate was significantly higher than following a short one (P = 0.03, T(3) = −3.78, paired t-test). Shading, ±s.e.m. g Correlation between REM episode duration and vlPAG firing rate during the subsequent inter-REM interval. Each dot represents activity of a unit during a single inter-REM interval (n = 40). Line, linear fit (R = 0.50, P = 0.001, T(38) = 3.58). h Correlation between vlPAG firing rate during inter-REM interval and duration of the interval. Line, linear fit (R = 0.63, P = 1.6 × 10−5, T(38) = 4.95)