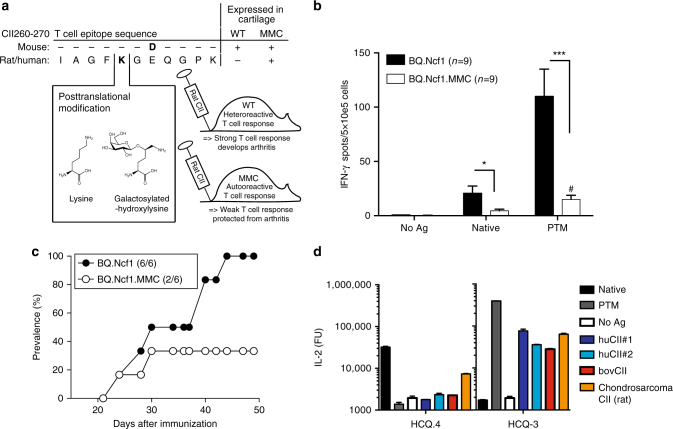
Fig. 1.
Summary of the autologous CIA model. a The MMC mouse expresses the immunodominant T cell epitope of heterologous (rat/human) CII as a self-antigen in the cartilage. A D266E amino acid substitution is the only difference between mouse and heterologous CII. A lysine at position 264 can become post-translationally modified by hydroxylation (not shown) and subsequent glycosylation with a monosaccharide. These modifications are recognized by distinct T cell clones (shown in d). MMC mice are immunized with heterologous CII (in this study rat CII) in order to induce an autoreactive T cell response. b The Ncf1 mutation was inserted onto the BQ background in order to render arthritis susceptibility in MMC mice. IFN-γ ELISPOT of lymph node cells isolated 10 days after immunization with rat CII and following re-stimulation with the non-modified (native) or glycosylated (PTM) CII peptide are shown. Bars indicate the mean number of spots ± SEM. #Statistical significance (p = 0.0195) between native and PTM responses in BQ.Ncf1.MMC mice, using a Wilcoxon's test. c Arthritis susceptibility of MMC mice in the BQ.Ncf1 background is reduced but not completely abrogated, when compared to non-MMC littermates. Number in brackets indicates cumulative number of animals that developed arthritis over total number of animals. d IL-2 production of T cell hybridoma clones specific to either the non-modified (HCQ.4) or PTM (HCQ.3) variants of the CII260–270 epitope after stimulation with the different peptides as well as whole CII protein obtained from different species (hu, human (two independent preparations/samples); bov, bovine (calf) CII from joint cartilage. The chondrosarcoma is a rat tumor line that was used as a positive control as it produces CII that is very heterogeneous in terms of PTMs19). Mann–Whitney U test was used in ELISPOT assays. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001