Figure 2.
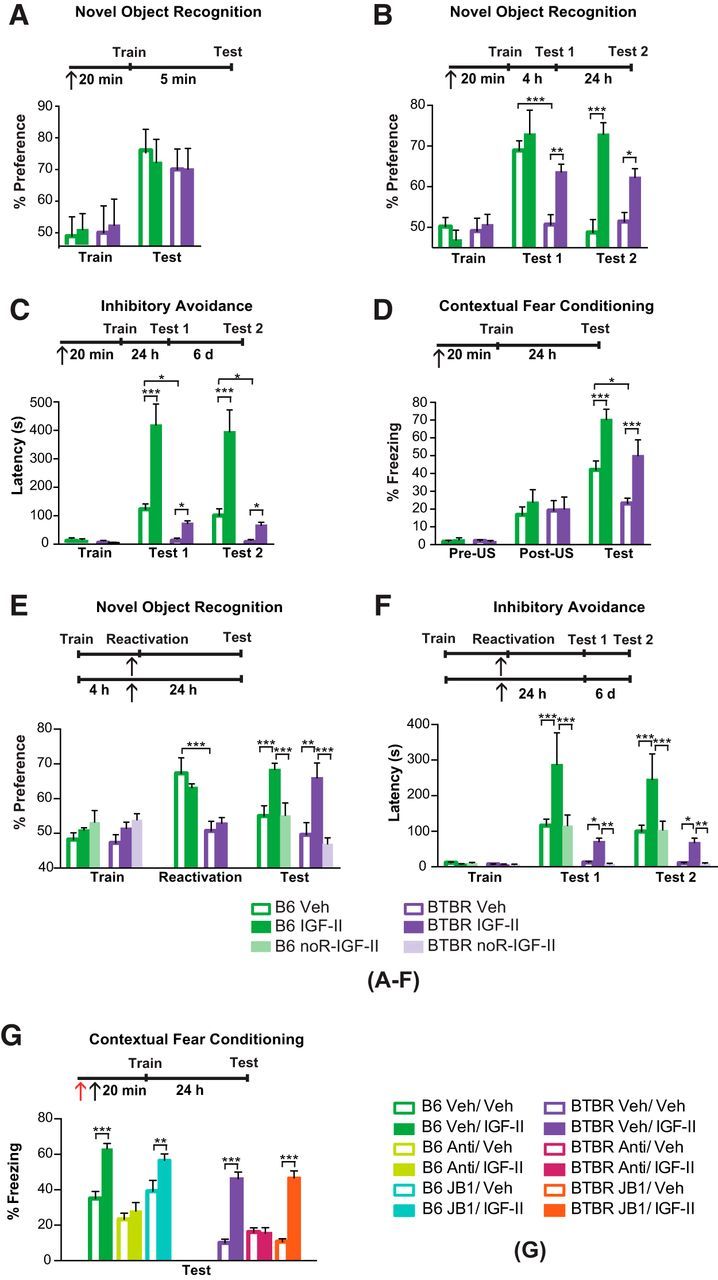
IGF-II reverses memory deficits of BTBR mice via hippocampal IGF-IIR. Experimental timelines are shown above graphs. In all experiments mice received a subcutaneous injection of either vehicle (Veh) or IGF-II (↑) 20 min before either training or memory reactivation as indicated. All data are expressed as the mean (±SEM). n = 7–8 per group. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc tests. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. See Extended Data table (Fig. 2-2) for detailed statistical analyses. A, B, Percentage exploration preference for a novel object compared with a familiar object during novel object recognition training (Train) and testing conducted 5 min (A), 4 h (B, Test 1), or 24 h (B, Test 2) after training of B6 and BTBR mice. C, Latency of B6 and BTBR mice injected with Veh or IGF-II prior IA training (Train). Mice were tested at 24 h after training (Test 1) and again 6 d later (Test 2). D, Percentage of time spent freezing before (Pre-US) or after (Post-US) the shock delivery during contextual fear conditioning training and testing at 24 h after training (Test) of B6 and BTBR mice injected with Veh or IGF-II. E, Percentage exploration preference for a novel object compared with a familiar object during novel object recognition of B6 and BTBR mice injected with Veh or IGF-II 20 min before reactivation, which consisted in a full test session given 4 h after training (Train). Test was conducted 24 h after the reactivation. F, IA latency of B6 and BTBR mice during training (Train), Test 1 conducted 24 h after reactivation and Test 2 conducted 6 d after Test 1. Reactivation consisted in 30 s exposure to the context. G, Percentage of time spent freezing during CFC testing (Test) of B6 and BTBR mice, which received a bilateral dorsal hippocampal injection (↑) of IGF-IR blocker (JB1), IGF-IIR functionally blocking antibody (Anti), Veh, or IgG immediately before a subcutaneous injection of either Veh or IGF-II. Test was conducted 24 h after training. Exploration times are shown in the Extended Data (Fig. 2-1), and detailed statistical analyses are reported in the Extended Data tables (Figs. 2-2 and 2-3).
