Figure 4.
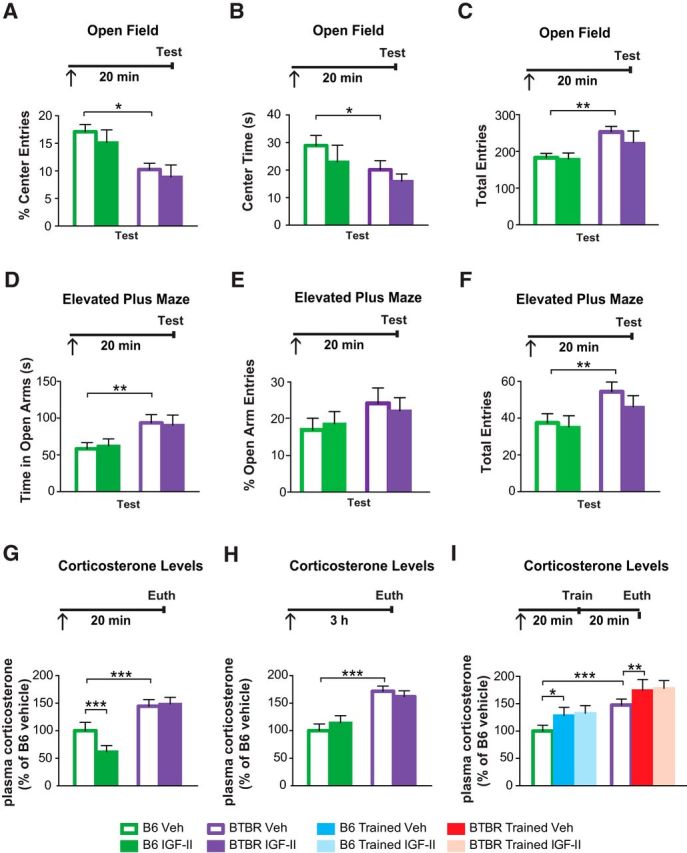
IGF-II does not change anxiety responses in BTBR mice. Experimental timelines are shown above graphs. In all experiments mice received a subcutaneous injection (↑) at the indicated time before behavioral assessment or euthanasia (Euth), as specified in each experiment. All data are expressed as the mean (±SEM). n = 7–8 per group. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc tests. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. A, Percentage of center entries, (B) time spent in the center, and (C) total entries into the center of an open-field by B6 and BTBR mice following a subcutaneous vehicle (Veh) or IGF-II injection given 20 min before Test. D, Time spent in the open arms, (E) percentage of entries into the open arms, and (F) total entries into the open arms of an elevated plus maze by B6 and BTBR mice 20 min following Veh or IGF-II injection. G, H, Relative concentration of plasma corticosterone (normalized to the levels of B6 untrained mice) of untrained B6 and BTBR mice 20 min (G) or 3 h (H) following a subcutaneous injection of Veh or IGF-II. I, Relative concentration of plasma corticosterone (normalized to levels of B6 untrained mice) of untrained or CFC-trained B6 and BTBR mice, which received a subcutaneous injection of Veh or IGF-II and were killed (Euth) 20 min after training or at the matched time point for untrained mice. For detailed statistical analyses see the Extended Data table (Fig. 4-1).
