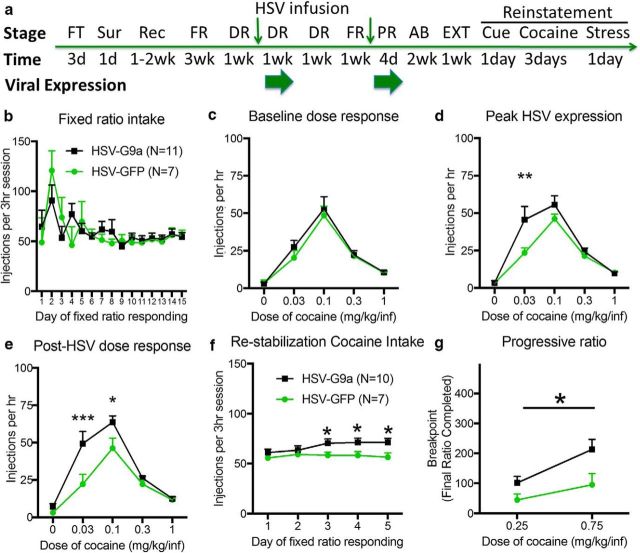
Figure 2.
G9a overexpression increases cocaine SA behaviors. a, Experimental time course depicting operant training with food pellets (FT), surgery (Sur), recovery (Rec), and fixed ratio (FR) cocaine SA training, followed by FR dose–response (DR) testing before, during, and after HSV-mediated expression of HSV-GFP or HSV-G9a. A second HSV infusion is given prior cocaine SA testing on a PR reinforcement schedule. Small green arrows represent HSV infusion times after counterbalancing groups for cocaine intake and dose–response; large green arrows represent viral expression periods limited to FR dose–response and progressive ratio testing. Extinction (EXT) and reinstatement tests were performed after a 2-week abstinence period (AB). b, Average cocaine reinforcers in study groups during cocaine SA acquisition/stabilization training before HSV infusions. c, FR dose–response testing before (c), during (d), and after (e) peak HSV-mediated expression of GFP or G9a (HSV-GFP: n = 7, HSV-G9a: n = 11). f, Restabilization of cocaine SA after the first HSV infusion. g, Cocaine SA on a PR schedule during GFP or G9a expression after a second HSV infusion. HSV-GFP: n = 7, HSV-G9a: n = 10. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 compared with HSV-GFP.