Figure 10.
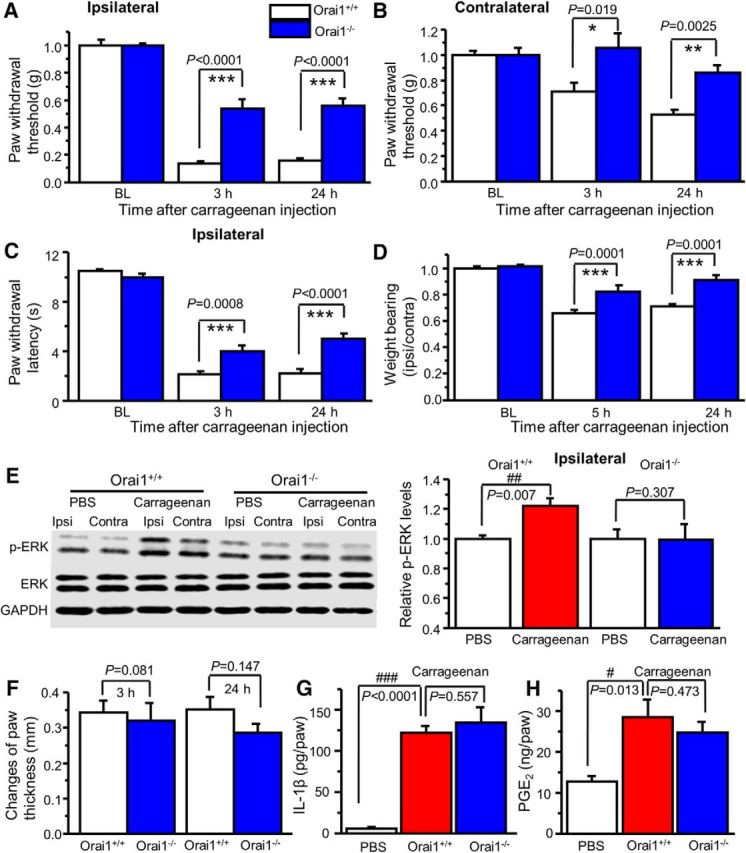
Orai1 deficiency attenuates carrageenan-induced pain hypersensitivity. A, B, Carrageenan-induced mechanical hypersensitivity in the ipsilateral paw (A) and the contralateral paw (B) from Orai1+/+ and Orai1−/− mice. Two-way ANOVA revealed significant differences between genotypes in the ipsilateral paw (F(1,13) = 35.0, p < 0.0001) and the contralateral paw (F(1,13) = 16.7, p = 0.0013). C, Carrageenan-induced thermal hypersensitivity in the ipsilateral paw. Two-way ANOVA revealed significant differences between genotypes (F(1,13) = 16.4, p = 0.0014). D, Weight distribution in Orai1+/+ and Orai1−/− mice. Two-way ANOVA revealed significant differences between genotypes (F(1,13) = 49.7, p < 0.0001). E, Carrageenan-induced ERK activation in the ipsilateral dorsal horn from Orai1+/+ mice, but not from Orai1−/− mice (p values are indicated in the graph). Ipsi, Ipsilateral; Contra, Contralateral. F, Paw thickness changes induced by intraplantar injection of carrageenan in Orai1+/+ and Orai1−/− mice. G, H, Carrageenan-induced IL-1β (G) and PGE2 (H) production in the injected paw from Orai1+/+ and Orai1−/− mice. Values are means ± SEM (n = 6–9 mice; p values indicated in the graph). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with Orai1+/+ mice; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 compared with the PBS group by the Student's t test or one-way ANOVA.
