Figure 6.
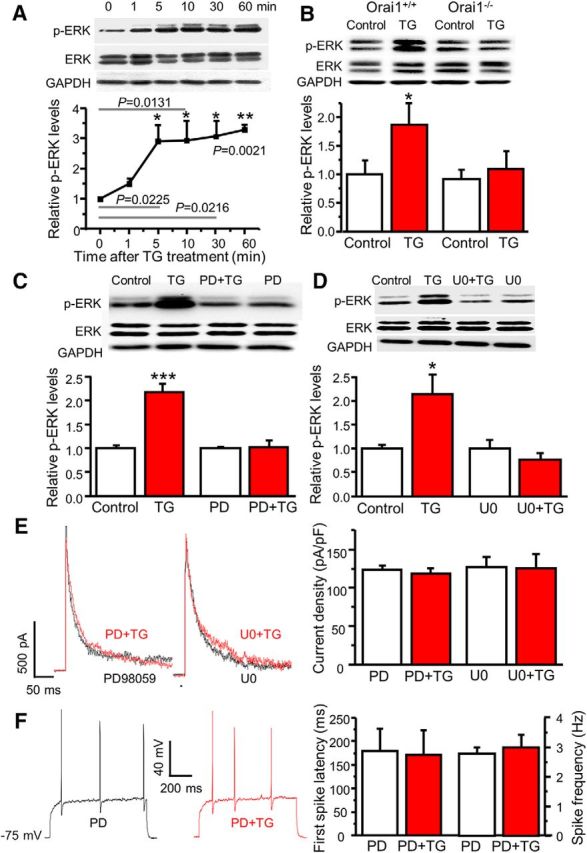
SOCs mediate modulation of A-type currents via ERKs. A, The time course of TG-induced ERK activation (n = 4, F = 67.7, p values indicated in the graph). B, TG-induced ERK activation in cultured dorsal horn neurons from Orai1+/+ and Orai1−/− littermates. For Orai1+/+ mice, n = 7 samples, df = 6, t = 3.25629, p = 0.0173; for Orai1−/− mice, n = 7 samples, df = 6, t = 0.990, p = 0.360. C, The effects of PD98059 (PD) on TG-induced ERK activation. For vehicle treatment, n = 10 samples, df = 9, t = 6.43439, p = 0.00012; for PD treatment, n = 8 samples, df = 7, t = 0.072, p = 0.944. D, The effects of U0126 (U0) on TG-induced ERK activation. For vehicle treatment, n = 4 samples, df = 3, t = 4.42385, p = 0.02145; for U0 treatment, n = 4 samples, df = 3, t = 2.415, p = 0.0946. E, The effects of PD and U0 on TG-induced modulation of A-type currents. For PD treatment, n = 9 neurons, df = 8, t = 1.289, p = 0.233; for U0 treatment, n = 7 neurons, df = 6, t = 0.206, p = 0.843. F, The effects of PD on TG-induced modulation of action potentials. For the first-spike latency, n = 8 neurons, df = 7, t = 0.760, p = 0.472. For spike frequency, n = 8 neurons, df = 7, t = 1.000, p = 0.351. Values are means ± SEM, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with control by the two-sample or paired-sample Student's t test.
