Figure 1.
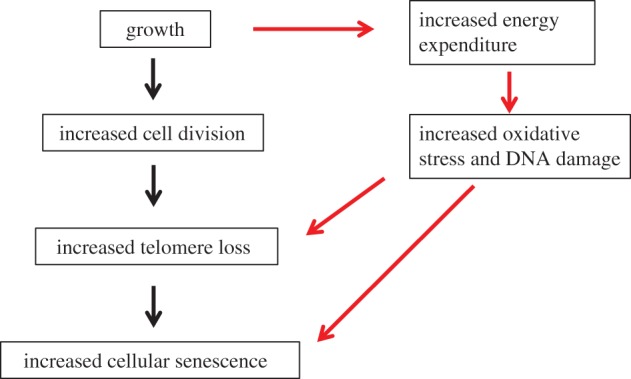
The routes whereby growth and telomere loss can be linked. The main route via increased cell division and the route via increased energy expenditure are shown. While normal growth will involve energy expenditure, organisms may have evolved strategies to minimize oxidative damage during this time. However, when circumstances favour more or faster growth, oxidative damage to DNA may occur as a result of the further increase in expenditure. Oxidative damage to telomeric DNA can increase the telomere loss per round of cell division, and increase the rate at which cells senesce. This oxidative damage may also trigger a persistent DNA damage response in the cell, triggering cell senescence directly in the absence of increased telomere loss. (Online version in colour.)
