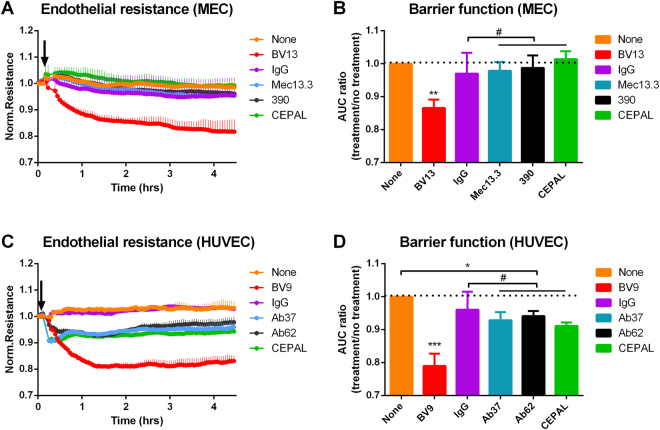
Figure 1.
Barrier function assay in mouse and human endothelial cells. Electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) measurement of endothelial resistance. (A and C) Real time tracings (representative of 4 independent monolayers) in MECs and HUVECs starting at the time of addition of specific antibodies or isotype controls. Presented resistance is normalized to a pre-treatment time-point for comparison of mAb effect on barrier function. (B) Quantification of AUC normalized to no treatment control. Anti-PECAM-1 antibodies had no effects on the electrical resistance of MEC monolayers in comparison to no treatment or isotype control (#p = 0.97, 0.99 for solo mAbs and 0.51 for a combination, respectively). Data shown as mean ± SD, dotted line illustrating a level of no treatment control. (D) In quiescent HUVEC cells, binding to PECAM-1, both solo and paired, results in significant drop in endothelial resistance (*p < 0.01, compared to no treatment). Effect mAbs to PECAM-1, when compared to IgG isotype control, was not significant (#p = 0.36 for Ab62 vs. mouse IgG2A and p = 0.81, for Ab37 vs. mouse IgG1). In both systems, significant barrier disruption was seen after binding of mAb to VE-cadherin (**p = 0.0005; ***p < 0.0001, compared to IgG isotype control). Data shown as mean ± SD, dotted line illustrating a level of no treatment control.