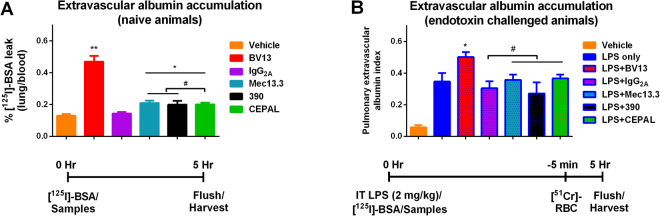
Figure 3.
Extravascular albumin accumulation of radiolabeled albumin in lungs of naïve (A) and endotoxin challenged (B) mice. Samples of mAbs were injected intravenously just after injection of [125I]-BSA. (A) Anti-PECAM-1 mAbs 390 and Mec13.3 both cause significant elevation of BSA leakage in comparison to isotype control, IgG2A, as does the mixture of CEPAL antibodies (*p = 0.02, 0.04, and 0.04 for Mec13, 390, and CEPAL, respectively). Collaborative binding does not cause any additional effect, however, as compared to solo antibodies (#p = 0.76 and p = 0.95 vs Mec13 and 390, respectively). Anti-VE-Cadherin mAb, in contrast, caused significant vascular leak (**p < 0.0001, compared to IgG2A control). Data shown as mean ± SD. (B) Neither anti-PECAM-1 antibodies nor CEPAL mixture exacerbate vascular leakage in animals treated with intratracheal LPS (#p = 0.87, 0.23, and 0.74, respectively), whereas anti-VE-Cadherin results in further compromise of endothelial barrier function (*p = 0.02 compared to LPS + IgG2A control). Pulmonary extravascular albumin index (Equation 1) is calculated as described in Materials and Methods, with data shown as mean ± SD.