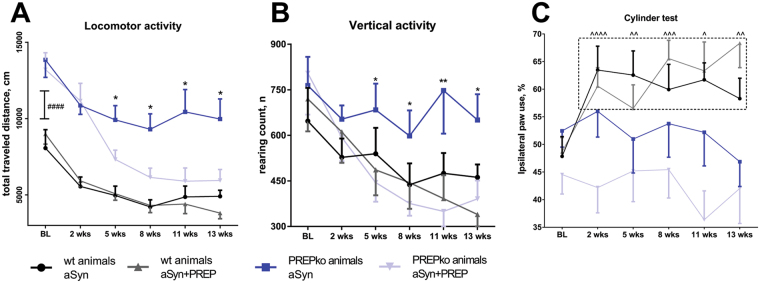
Figure 1.
PREPko mice after viral injection of aSyn showed behavioral resistance to aSyn toxicity. (A) Total traveled distance was significantly reduced in PREPko animals with aSyn + PREP injection compared to PREPko animals with only aSyn at the 5-week time point and the difference extended until the end of the experiments. BL locomotor activity was drastically higher in PREPko compared to wt animal groups (n = 7–10). (B) Similar to total distance travelled, vertical activity was statistically different between PREPko animal groups starting from the 5-week time point and the difference extended until the end of the experiments (n = 7–10). (C) Unilateral aSyn viral vector injection caused increased ipsilateral paw use 2 weeks after injection only in the wt animal groups (n = 15–17), and this difference was not seen in PREPko animals. Bars represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, PREPko aSyn vs. PREPko aSyn + PREP; ####p < 0.0005, wt vs. PREPko; ^p < 0.05, ^^p < 0.01, ^^^p < 0.001, ^^^^p < 0.0005, wt animal BL vs. post-injection measurements (2-way ANOVA with Univariate analyses; Student’s t-test for BL locomotor activity).