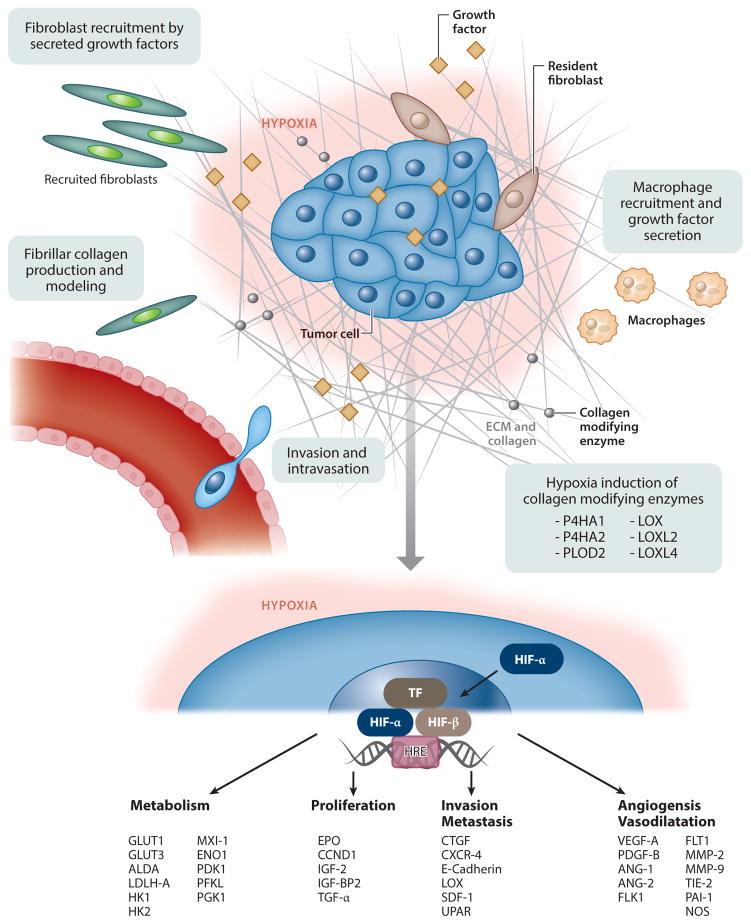
Figure 1.
Cancerous pathways affected by accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF). Abbreviations: ALDA, aldolase A; ANG-1, angiopoietin 1; ANG-2, angiopoietin 2; BMDSC, bone marrow–derived stem cell; CCND1, cyclin D1; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; CXCR-4, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; ECM, extracellular matrix; ENO1, enolase 1; EPO, erythropoietin; FLK1, VEGF receptor 2; FLT-1, VEGF receptor 1; GLUT, glucose transporter; HK, hexokinase; IGF-2, insulin growth factor 2; IGF-BP2, insulin-like growth factor–binding protein 2; LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase A; LOX, lysyl oxidase; miRNA, microRNA; LOXL, lysyl oxidase homolog 1; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MXI-1, max interactor 1; P4HA, prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit α1; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1; PDGF-B, platelet-derived growth factor B; PDK1, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1; PFKL, phosphofructokinase L; PGK1, phosphoglycerate kinase 1; PLOD, procollagen-lysine 2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase; SDF-1, stromal cell–derived factor 1; TF, transcription factor; TGF-α, transforming growth factor α; TIE-2, angiopoietin receptor 2; UPAR, urokinase plasminogen activator receptor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor. Modified from Reference 46.