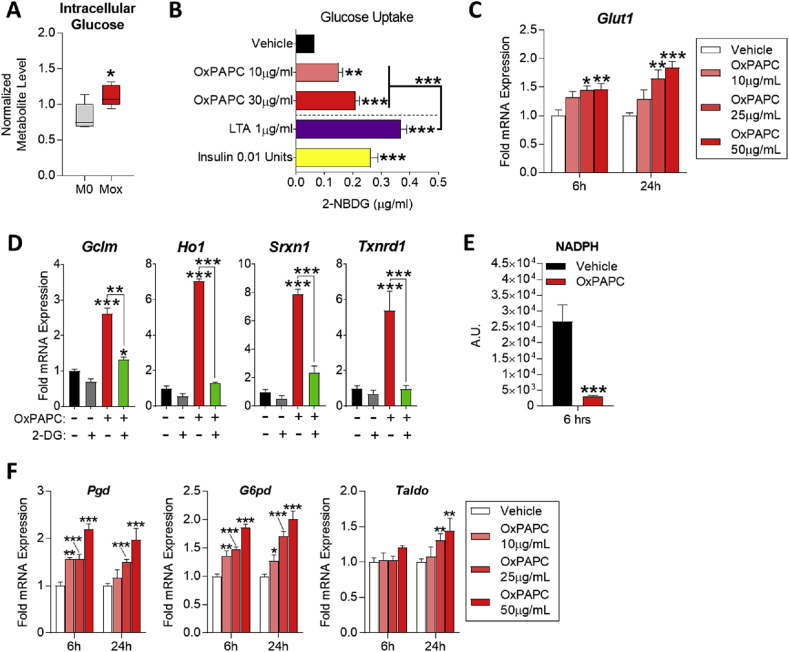
Figure 2.
OxPL-treated macrophages induce the pentose phosphate pathway while relying on glucose metabolism for antioxidant gene expression. A. Intracellular glucose levels from metabolomics of polarized BMDMs represented by box and whisker plots (n = 5). B. Glucose uptake in BMDMs treated with vehicle (RPMI media), 10–30 μg/mL OxPAPC, 1 μg/mL LTA, or 0.01 units of insulin for 6 h. Uptake measured by fluorescence quantification of 2-NBGD (2-(N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)amino)-2-deoxy-glucose; fluorescent 2-deoxy-glucose analog) (n = 4). C.Glut1 mRNA expression as measured by qPCR in RAW264.7 cells after 6 and 24 h treatment with vehicle (RPMI media) or 10–50 μg/mL OxPAPC (n = 4). D. mRNA expression of redox homeostasis genes measured by qPCR in BMDMs after 4 h treatment with 10 μg/mL OxPAPC and/or 10 mM 2-deoxy-d-glucose (2-DG) (n = 3). E. Intracellular NADPH levels in BMDMs treated with 10 μg/mL OxPAPC for 6 h, measured using the NADP/NADPH Assay Kit (Abcam; ab65349) (n = 4). F. mRNA expression of pentose phosphate pathway genes measured by qPCR in RAW264.7 cells treated with 10–50 μg/mL OxPAPC for 6 or 24 h. Genes measured include Pgd, G6pdx, and Taldo (n = 4). G. mRNA expression of metabolism-related genes measured by qPCR in BMDMs after 24 h treatment with 6.4 μM (50 μg/mL) OxPAPC, OxPAPE, or OxAA (n = 3). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Biological replicates indicated by (n). Statistical significance calculated by Welch's 2-sided t-test (*p ≤ 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).