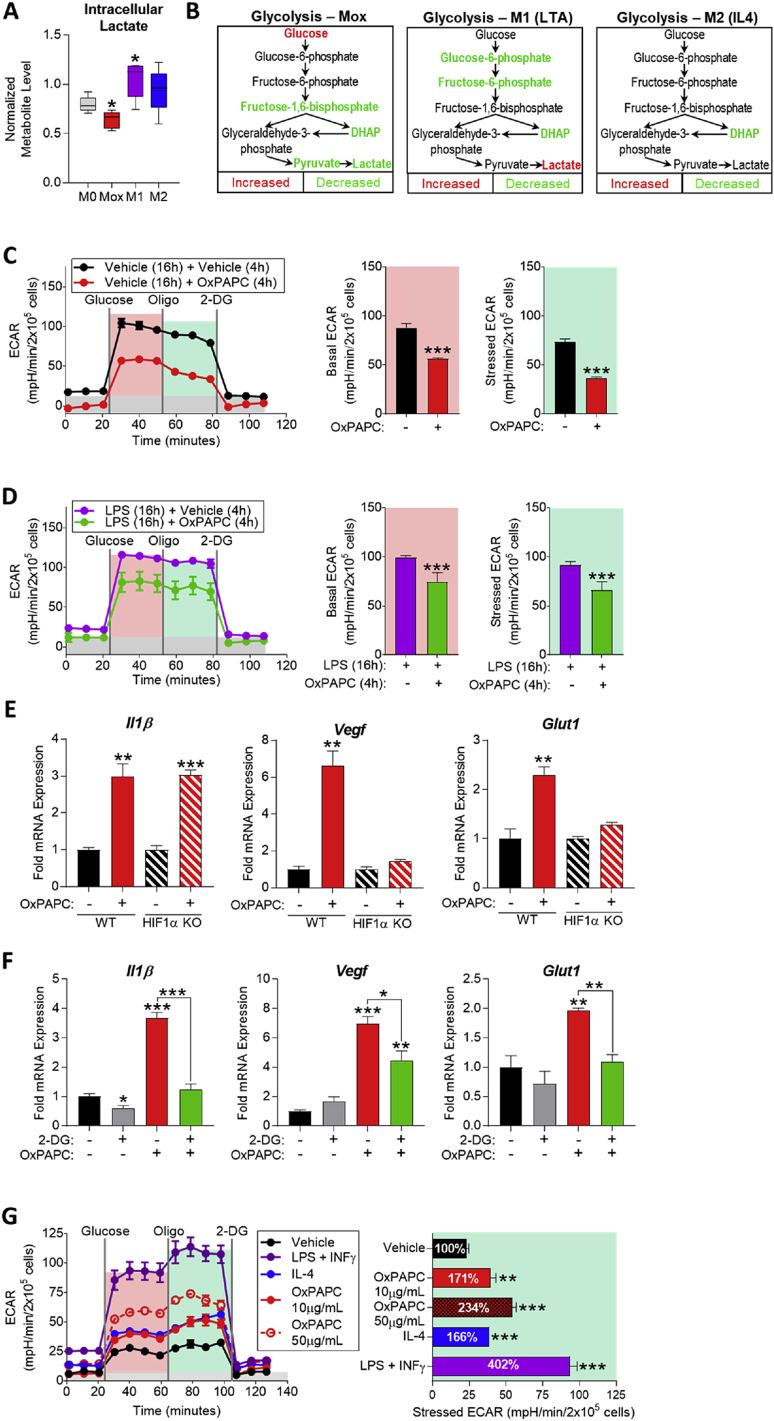
Figure 3.
The macrophage metabolic adaptation to OxPLs involves transient suppression of aerobic glycolysis and HIF1α-dependent and independent gene expression. A. Intracellular lactate from metabolomics of M0 (vehicle, RPMI media), Mox (10 μg/mL OxPAPC), M1 (1 μg/mL LTA), and M2 (10 ng/mL IL4) BMDMs (6 h) represented by box and whisker plots (n = 5). B. Glycolysis pathway in Mox, M1, and M2 BMDMs (6 h) (n = 5). C. Glycolytic stress test (GST) of BMDMs treated with vehicle (RPMI media) or 10 μg/mL OxPAPC for 4 h (n = 4). The extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) was measured after injection of 20 mM glucose, 1 μM oligomycin, and 80 mM 2-DG addition to produce the basal (red), stressed (teal), and background (gray) ECAR, respectively. Basal and stressed ECAR were calculated by subtracting the mean ECAR of the post-glucose (basal) or post-Oligomycin (stressed) measurements from the mean ECAR of the post-2-DG measurements. D. GST of BMDMs treated with 1 μg/mL LPS for 16 h to induce M1 polarization, followed by 4 h treatment of vehicle (RPMI media) or 10 μg/mL OxPAPC (n = 4). E. mRNA expression of Il1β, Vegf, and Glut1 measured by qPCR in WT and HIF1α-KO BMDMs treated with vehicle or 50 μg/mL OxPAPC for 6 h (n = 4). F. mRNA expression of Il1β, Vegf, and Glut1 measured by qPCR in WT BMDMs treated with 10 mM 2-DG and/or 10 μg/mL OxPAPC for 4 h (n = 3). G. GST of BMDMs treated with vehicle, 1 μg/mL LPS (M1), 10 ng/mL IL4 (M2), or 10–50 μg/mL OxPAPC (Mox) for 24 h (n = 4). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Biological replicates indicated by (n). Statistical significance calculated by Welch's 2-sided t-test (*p ≤ 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).