Figure 3.
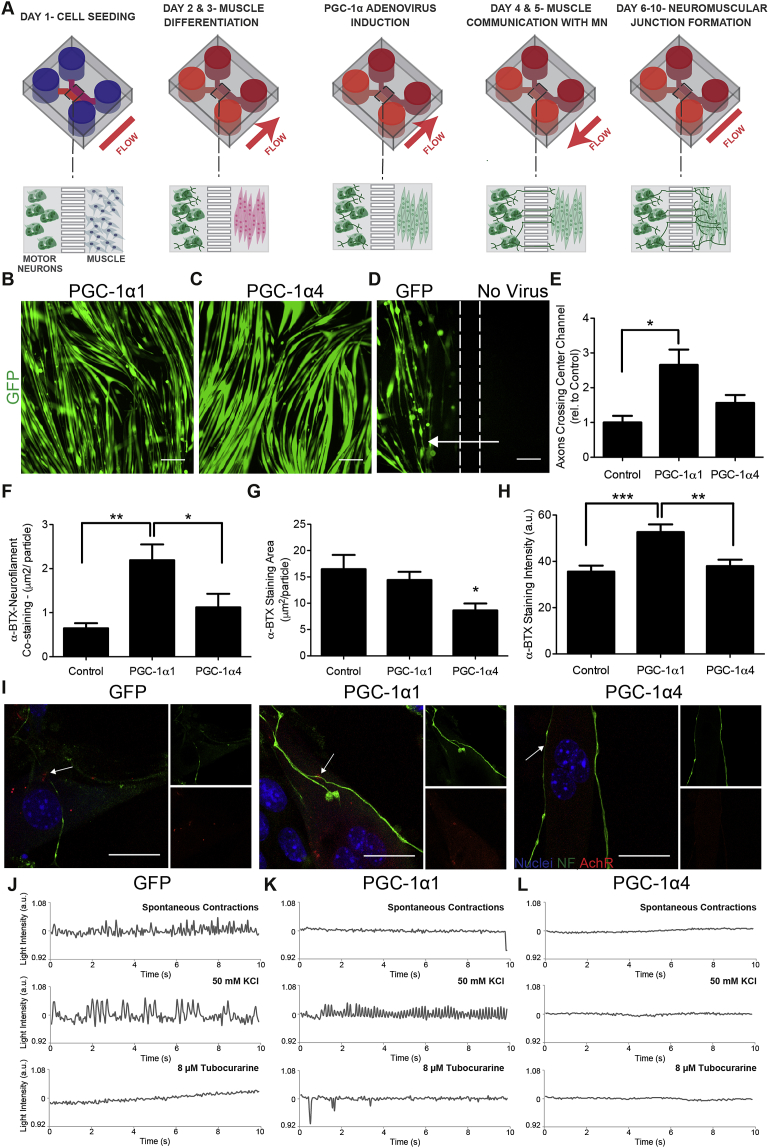
Expression of PGC-1α isoforms in muscle modulates axonal recruitment and NMJ morphology. A) Schematic of NMJ model with forced expression of PGC-1α1, PGC-1α4 and GFP. Experimental set-up was the same as in Figure 1 with the additional step of PGC-1α/GFP adenovirus transduction. After myotube differentiation, expression of PGC-1α1, PGC-1α4, and GFP was induced via an 8-hour viral transduction. During this time, media flow was directed from the motor neurons towards the muscle, fluidically isolating the myotubes and restricting the adenovirus to the muscle compartment. After virus transduction, muscle cells were washed and the media flow was reversed, flowing from the muscle side towards the motor neurons, allowing the muscle to ‘communicate’ with the motor neurons (days 4 & 5). Expression of B) PGC-1α1 and C) PGC-1α4 in myotubes using adenovirus induction. Scale bars represent 200 μm in B–D. D) Myoblasts were seeded and differentiated within both cell culture compartments, and GFP control adenovirus was added to one compartment (left side), while the flow was tailored towards the treated side (arrow). Only the treated compartment expressed GFP, demonstrating fluidic isolation during virus transduction. Dashed lines represent the approximate location of the microchannels. E) Motor neuron recruitment in response to overexpression of PGC-1α1, PGC-1α4 and GFP in myotubes. Data quantifies the number of axons crossing central channel at day 6 and is presented as mean ± SEM relative to GFP control for n = 4 experiments with 2–3 devices per condition of each experiment. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post-hoc test, (*) p < 0.05. F) Mean area of co-staining of neurofilament and α-bungarotoxin (α-BTX), G) mean area of AchR clusters as determined by α-BTX staining, and H) mean intensity of α-BTX staining. Data represents mean ± SEM for n = 3 experiments. Statistical significance was determined using a Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's post-hoc test, (**) p < 0.01, (***) p < 0.001. I) Immunolocalization of neurofilament (NF) (green), AchR stained with α-BTX (red) and cell nuclei (blue). Smaller images show neurofilament (top) and α-BTX (bottom) staining individually. Arrows indicate NMJs. Scale bar represents 20 μm. Functional analysis of NMJ formation after myotubes were treated with J) GFP control, K) PGC-1α1 and L) PGC-1α4 adenoviruses. Graphs show muscle fibre contractions (as measured by changes in light intensity) during standard culture (spontaneous contractions), after motor neuron stimulation with 50 mM KCl, and after NMJ inhibition with 8 μM tubocurarine.