Figure 4.
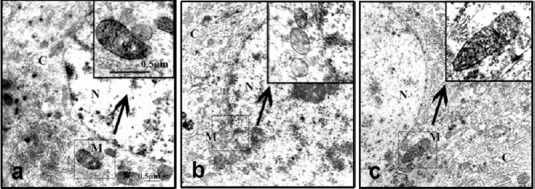
Ultrastructural changes in mitochondria and COX enzyme staining in hippocampal neurons in Alzheimer's disease rats treated with RCE (transmission electron microscopy).
(a) Normal control group; (b) model group; (c) M-RC group. (N: nucleus; C: cytoplasm; M: mitochondria). At 21 days after model establishment, the mitochondria in neurons in the hippocampal CA3 region were examined by COX enzyme histochemistry using electron microscopy. The high-electron-dense COX-positive precipitates accumulated in the mitochondrial inner membrane and cristae represent mitochondrial COX enzymatic activity. Rats in the normal control group showed intact mitochondria with large amounts of discernible COX-positive precipitates. The model group showed strikingly swollen mitochondria, a pale gray matrix, and ruptured or blurred cristae with fewer COX-positive precipitates. The M-RC group showed more COX-positive precipitates and less pathological changes in mitochondria compared to the model group. Inserts: Higher magnification of the boxed area in (a)–(c). Scale bar: 0.5 μm. COX: Cytochrome c oxidase; RCE: ethanol extract of Rhodiola crenulata root; M-RC: moderate-dose RCE.
