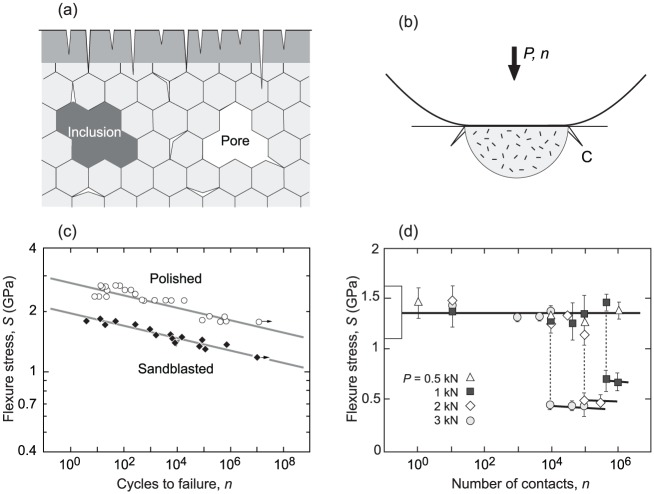
Figure 2.
Factors affecting durability of zirconia ceramics. (a) Schematic diagram showing flaws in ceramic structure: microcracks at internal grain boundaries and surface damage zone (shaded) from machining/sandblasting; pores and inclusions from sintering. (b) Schematic diagram of degradation from damage at surface from occlusal contact at load P (arrow) and number of cycles n, showing generation of quasiplastic zone with initiation of macroscopic cone-like crack (C) from microcrack coalescence. (c) Flexural stress versus number of cycles (S-n curve) for an ultrastrong 3Y-TZP in as-polished and heavily sandblasted states. Data from Zhang et al. (2004). (d) Static strength for a 3Y-TZP after repeat surface contact with a metal sphere (radius, 3.18 mm). Box at left axis designates laboratory strengths (unindented specimens, SD bounds). Data from Jung et al. (2000). Pronounced fatigue is apparent in both data sets. 3Y-TZP, 3 mol% yttria stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal.