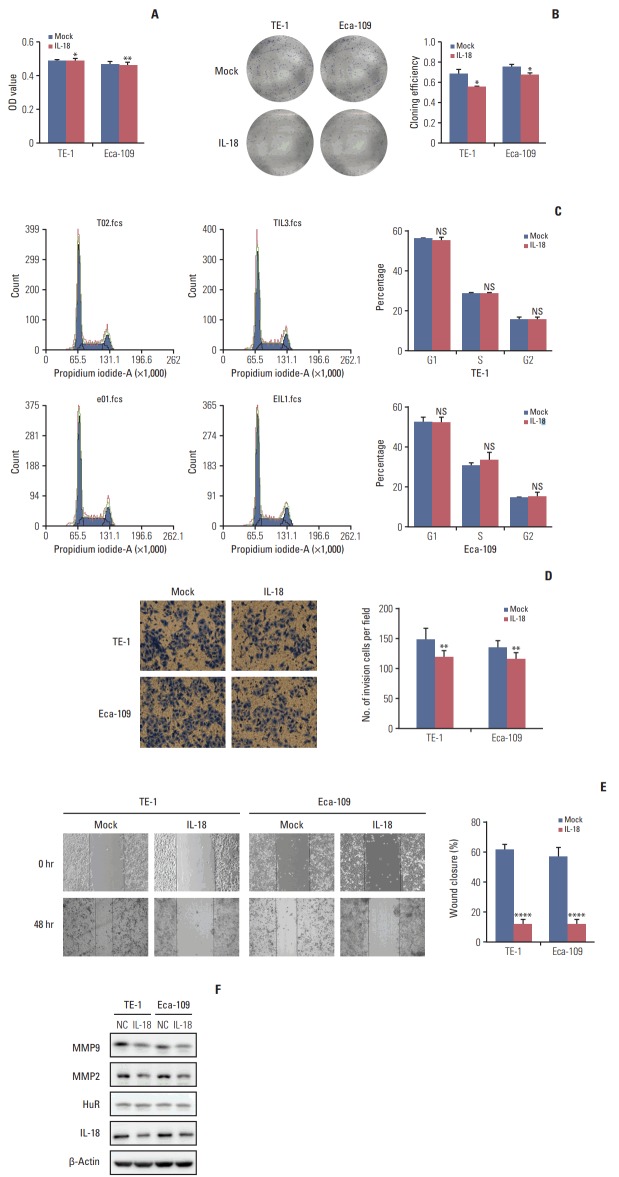
Fig. 6.
Interleukin 18 (IL-18) inhibited proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. (A) The effect of human antigen R (HuR) on the viability of TE-1 and Eca-109 cells seeded in 96-well plates and treated with IL-18 (5 ng/mL) for 48 hours were analyzed by 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). (B) Colony formation assays of TE-1 and Eca-109 cells treated with IL-18 (5 ng/mL). After 10 days, the cells were stained with crystal violet. Colonies consisting of more than 50 cells were counted. The data are presented as the mean±standard error of mean (SEM) (n=3). *p < 0.05 compared to the negative control. (C) TE-1 and Eca-109 cells were treated with IL-18 for 48 hours, and stained with propidium iodide in preparation for flow cytometry with the FACSCalibur system as described in Materials and Methods. (D) Migration of cells was assessed using a transwell assay. The TE-1 and Eca-109 cells treated for 48 hours with IL-18 were seeded in the upper chambers and incubated for 30 hours at 37°C. Then, the cells in the upper chambers were carefully scraped off using a cotton swab, and the ones that had migrated to the basal side of the membrane were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with Giemsa, and the membranes were mounted and dried at 37°C for 30 minutes (**p < 0.01). (E) Wound healing was observed 48 hours after the cells were treated with IL-18, and the open wound area after incubation was normalized to the initial wound area. The data are presented as the mean±SEM normalized to the control cells (****p < 0.0001). (F) Protein extracts from TE-1 and Eca-109 cells treated for 48 hours with IL-18 were subjected to Western blot analysis for HuR, IL-18, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2, and MMP9.