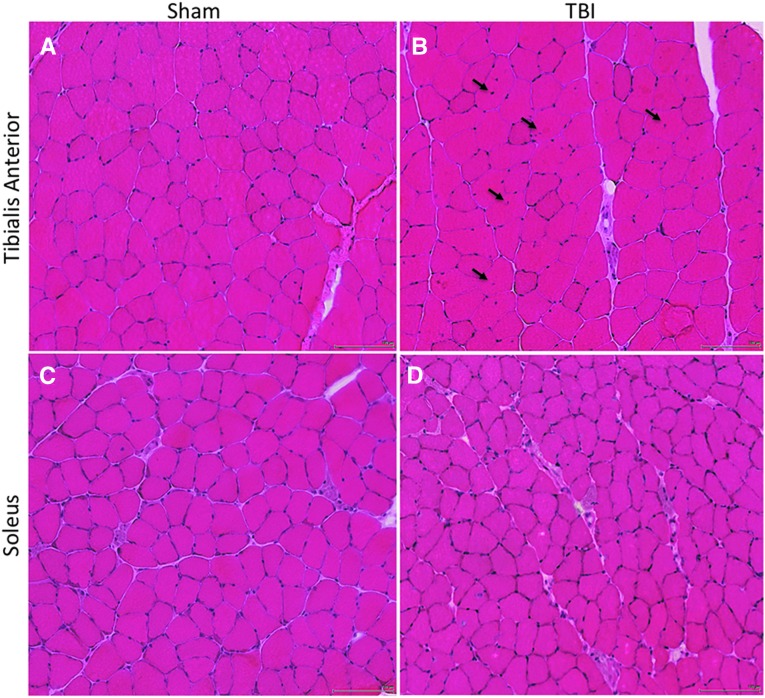
FIG. 1.
Hematoxylin and eosin–stained sections of the tibialis anterior (TA) muscle (A, B; top row) and soleus (Sol) muscle (C, D; bottom row) in Sham-injured mice (A, C; left column) and traumatic brain injury (TBI) mice (B, D; right column). Several centralized nuclei (black arrows) can be seen in the injured TA muscle (B), and smaller fiber areas can be appreciated in the injured Sol muscle (D), compared with sham-injured animals. Micrographs were obtained at 20 × magnification. Scale bar is 100 μm.