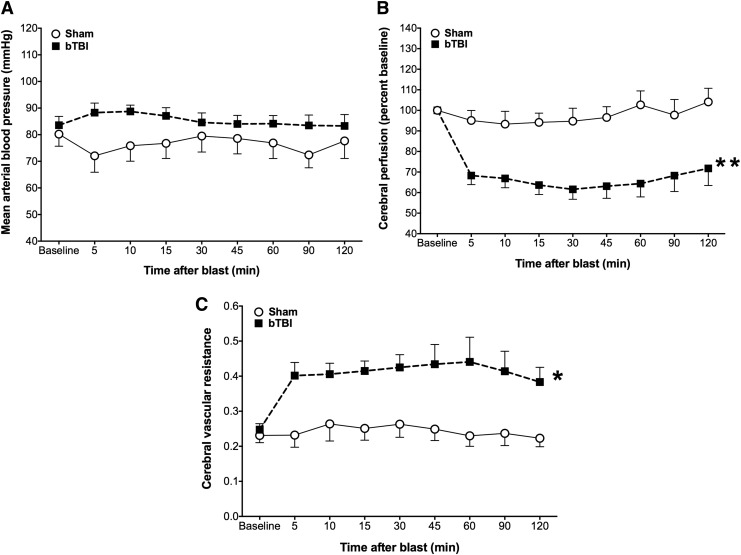
FIG. 4.
Effects of blast-induced traumatic brain injury (bTBI) (n = 12) or sham bTBI (n = 10) on mean arterial blood pressure (MAP), relative cerebral perfusion, and cerebral vascular resistance (CVR). (A) Although there was a trend toward elevated MAP in the bTBI group for at least 2 h after injury, the difference in MAP between the bTBI and sham group was not significant (p = 0.11, bTBI vs. sham). (B) Relative cerebral perfusion was significantly reduced in the bTBI group compared with the sham group for at least 2 h after bTBI whereas (C) CVR was significantly elevated in the bTBI group compared with the sham group for at least 2 h after bTBI. Values are plotted as means ± SEM. *p < 0.001 versus sham; **p < 0.0001 versus sham.