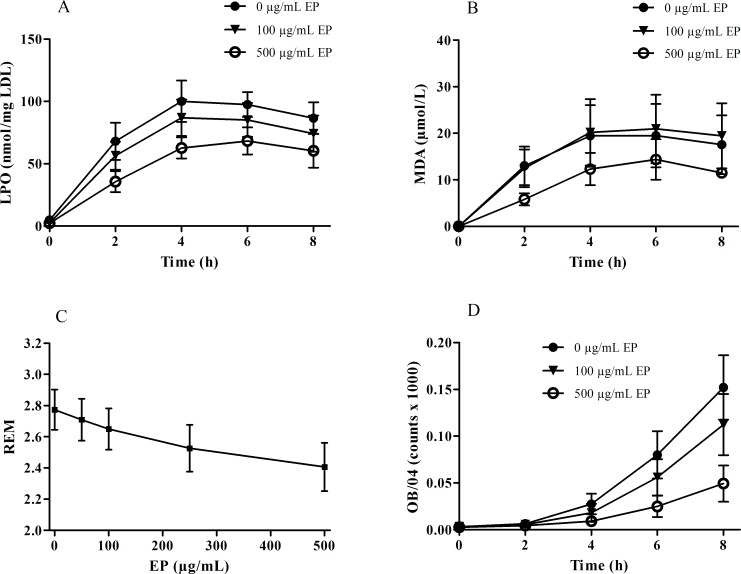
Fig 1. Effect of increasing amounts of EP on nLDL oxidation induced by Cu2+ ions in vitro.
nLDL (1.5 mg/mL) was preincubated in the absence or presence of EP (100 and 500 μg/mL) and then oxidized by addition of 10 μmol/L CuCl2 for up to 8 h. (A) EP significantly decreased LPO formation (p < 0.05), (B) MDA formation (p < 0.05), and (D) the amount of oxidation-specific epitopes (p < 0.05). (C) REM concentration-dependently decreased when LDL was oxidized in the presence of increasing amounts of EP (p < 0.005). Data represent mean ± SD from three separate experiments.