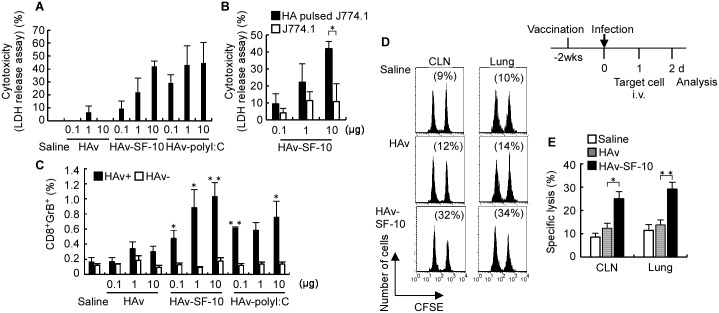
Fig 4. CTL-mediated cytolysis of target cells in vitro and in vivo.
CTL activity against J774A.1 target cells pulsed with HA peptide was measured using LDH release assay (A and B). BALB/c mice were immunized three times intranasally with HAv, HAv-polyI:C or HAv-SF-10 at the indicated doses of HAv (from 0.1 to 10 μg), and splenocytes were isolated for restimulation with HAv and IL-2 for use as effector cells. After 72 h co-culture of the effector cells with the HA peptide-pulsed or non-pulsed J774A.1 target cells at effector: target ratio of 20:1 for 5 h, cytolysis of the target cells was evaluated by LDH release assay. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM (%) (n = 4). The splenocytes of BALB/c mice immunized 3 times intranasally with HAv, HAv-polyI:C or HAv-SF-10 were isolated, and incubated with or without 10 μg/ml HAv for stimulation. After 72 h, splenocytes were analyzed for GrB production by intracellular staining (C). GrB producing cells on gated CD8+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM after incubation with HAv (+) or without HAv (-) in each immunization group (n = 4). P; versus the same dose of HAv. Two weeks (wks) after the third immunization, mice were infected with 100 × LD50 of PR/8, and then the target cells (5 × 106) were equally mixed with HA peptide-unpulsed CFSElow and pulsed CFSEhigh splenocytes were injected intravenously (i.v.) at 24 h after infection. The cytolysis of peptide-pulsed CFSE splenocytes in CLNs and lungs was analyzed by flow cytometry and calculated according to the formula described in the Materials and Methods (D and E). Data are representative of separate experiments (D). Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of HAv-SF-10, HAv and saline in CLNs and lungs (E) (n = 6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.