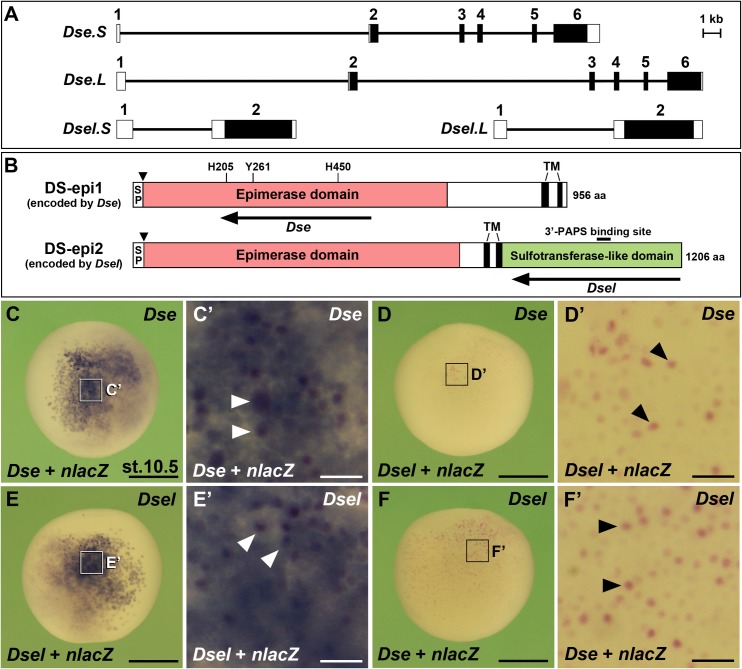
Fig 1. Genomic organization, protein structure and probe specificity of Dse/DS-epi1 and Dsel/DS-epi2 in X. laevis embryos.
(A) Genomic structures of the Dse and Dsel homeologs. Rectangles with numbers show exons and intervening lines demarcate introns. Filled boxes indicate open reading frames. Accession numbers of the Xenopus laevis genomic DNA / mRNA sequences are: DS-epi1.S, NC_030733 / KU877109; DS-epi1.L, NC_030732 / XM_018263281; DS-epi2.S, NC_030735 / XM_018223616; DS-epi2.L, NC_030734 / KU877110. (B) Overall protein structure of DS-epi1 and DS-epi2, which are encoded by Dse and Dsel, respectively. SP, cleavable signal peptide; TM, transmembrane domain. The arrows represent the antisense RNA probes of Dse and Dsel that were used for the in situ hybridization. (C-F’) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of early gastrula embryos in lateral view. The Dse probe detects injected Dse mRNA (C,C’) but not Dsel mRNA (D,D’). The Dsel probe specifically targets injected Dsel mRNA (E-F’). Arrowheads depict cells that received co-injected nlacZ mRNA as a lineage tracer (red nuclei). Each synthetic mRNA was injected at a dose of 100 pg into the animal pole of a single blastomere at the 4-cell stage. Scale bars are 500 μm (C-F) and 50 μm (C’-F’).