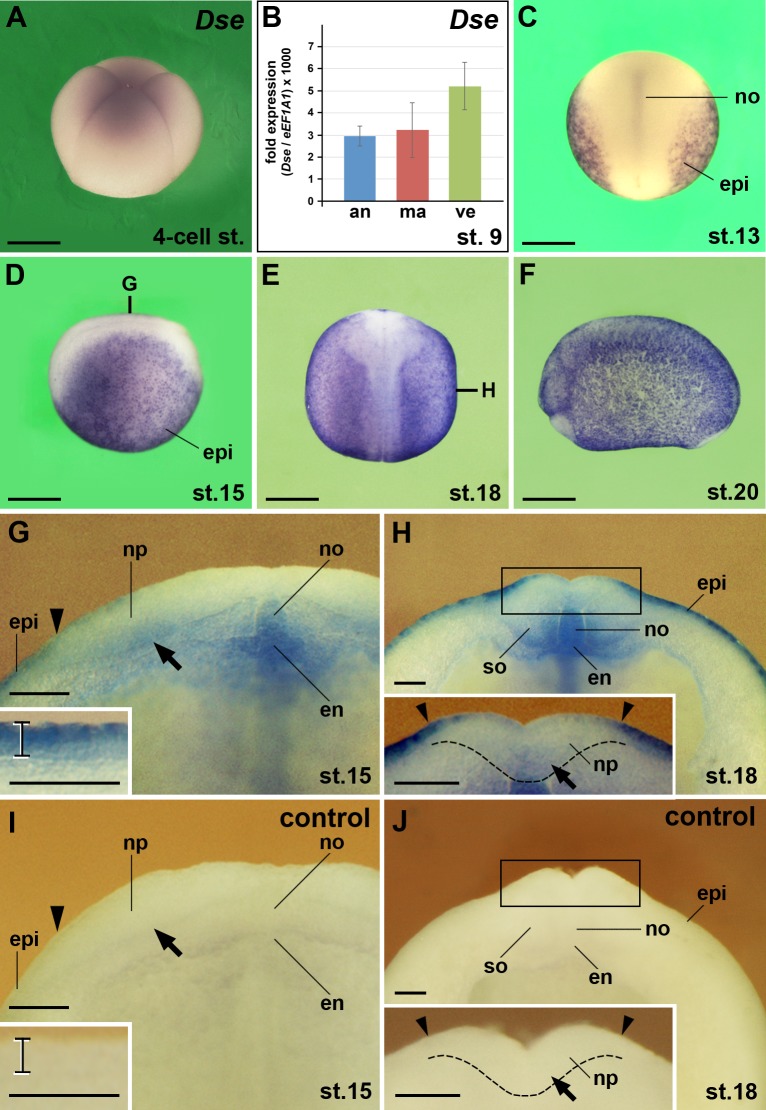
Fig 2. Dse mRNA is maternally deposited and expressed in the epidermis, neural ectoderm, notochord, somites and dorsal endoderm.
Xenopus embryos after whole-mount in situ hybridization in lateral view (A,D,F), dorsal view (C,E) and transversally sectioned through the anterior trunk (G-J). (A) Embryo at the 4-cell stage. Weak expression of Dse mRNA is visible. (B) qPCR analysis of embryonic explants at stage 9. Note Dse transcripts in the animal cap, marginal zone and vegetal region. (C) At stage 13, Dse is expressed in the epidermis and notochord. (D-F) Neurula embryos show ubiquitous Dse expression in the epidermis. The bold lines indicate the levels of sections in G and H. (G) Embryo at stage 15. The arrowhead indicates the border between epidermis and neural ectoderm. Note Dse transcripts in the sensorial layer of the lateral neural plate (arrow), notochord and dorsal endoderm. The bracket in the inset depicts the epidermis with robust Dse expression in the outer layer and lower mRNA levels in the inner layer. (H) Embryo at stage 18. Note Dse signals in the medio-ventral somites. The inset shows Dse expression in the sensorial layer of the ventral neural groove (arrow). The stippled line demarcates the border between the neural plate and the underlying dorsal mesoderm. (I,J) No signals appear in matching sections of sibling embryos that were probed with Dse sense RNA as control. an, animal cap; en, endoderm; epi, epidermis; ma, marginal zone; no, notochord; np, neural plate; so, somite; ve, vegetal region. Scale bars are 500 μm (A,C-F) and 50 μm (G-J).