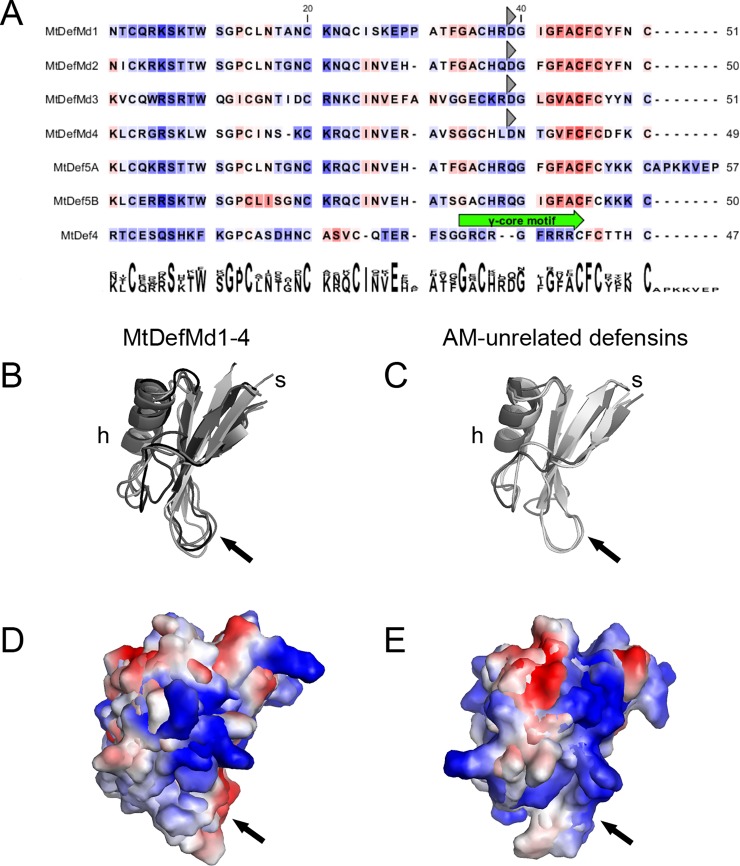
Fig 1. Sequence analyses of of AM-dependent defensins MtDefMd1-4 and AM-unrelated defensins.
Secondary structures of MtDefMd1-4 and AM-unrelated defensin-like proteins of M. truncatula (A), a representation of their three-dimensional structures (B and C), as well as surface electrostatics (D and E) are shown. Predicted signal peptides were removed from the mature amino acid sequences. Consecutively, the defensins were aligned based on their secondary structures. Background colorisation of the amino acids (in A) indicate hydrophobicity in a scale from red to blue (red: high hydrophobicity). A conserved aspartic acid in the C-terminal region of MtDefMds is marked with a grey triangel. For the bi-domain defensin MtDef5, the domains MtDef5A (including a 7 amino acid linker towards the MtDef5B domain) and MtDef5B are shown. After modelling the three-dimensional structures of the MtDefMd1-4, MtDef4 and MtDef5A/B defensins, they were visualized (B and C) and their surface electrostatics were calculated (D and E). The region congruent to the γ-core motif is indicated with arrows. The following proteins were used for comparisons in addition to MtDefMd1-4: MtDef5 A [65], MtDef5 B [65]and MtDef4 [30].