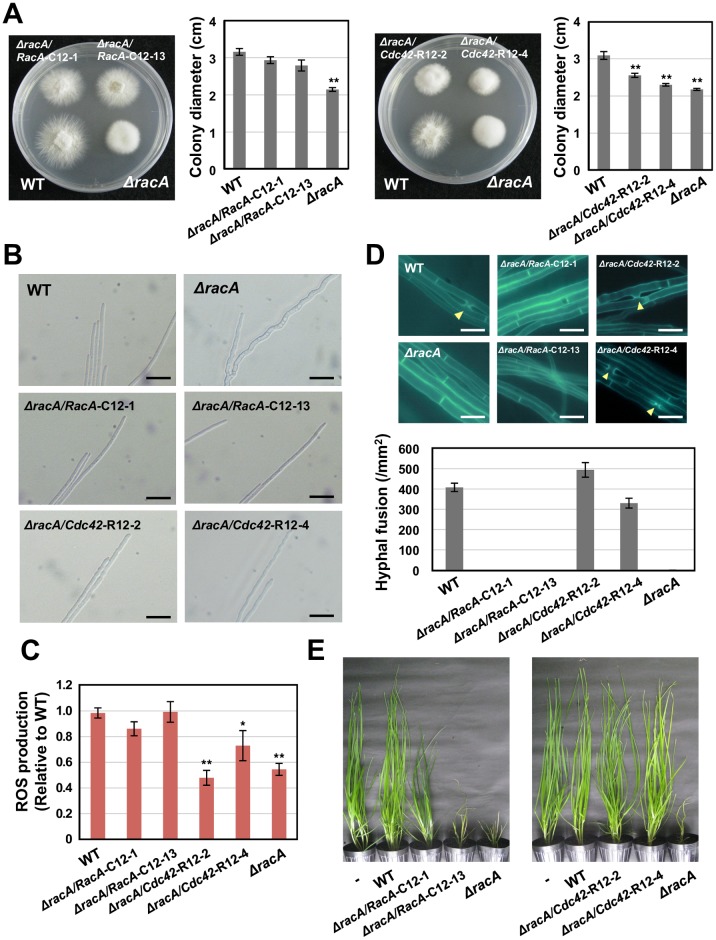
Fig 10. Binding of RacA/Cdc42 to NoxR is required for hyphal fusion and symbiotic infection of Epichloë festucae.
(A) Colony morphology and diameter of E. festucae wild type (WT), racA mutant and complemented strains on PDA grown for 10 days. Data are means ± standard error. n = 9. Data marked with asterisks are significantly different from wild type as assessed by two-tailed Student’s t tests: **P < 0.01. (B) Hyphal tip growth of WT, racA mutant and complemented strains on PD ager for 20 days. Bars = 20 μm. (C) L-012-mediated detection of ROS production by E. festucae WT, racA mutant and complemented strains. Colony edge of endophyte strains grown on PDA was treated with L-012 and ROS production was detected as chemiluminescence. Value of chemiluminescence relative to wild type was scored. Data are means ± standard error. n = 18. Data marked with asterisks are significantly different from wild type as assessed by two-tailed Student’s t tests: **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. (D) Hyphal fusion of E. festucae WT, racA mutant and complemented strains grown on water (top) E. festucae strains were grown on water agar for 10 days, stained with calcofluor white and monitored with fluorescence microscopy. Arrowheads indicate hyphal fusions. Bars = 10 μm. (bottom) The number of hyphal fusions of E. festucae strains grown on water agar. Data are means ± standard error from 30 sites from three colonies of each strain. (E) Phenotype of perennial ryegrass infected with E. festucae WT, racA mutant or complemented strains. Photographs were taken approx. 11 weeks after inoculation.