Fig. 3.
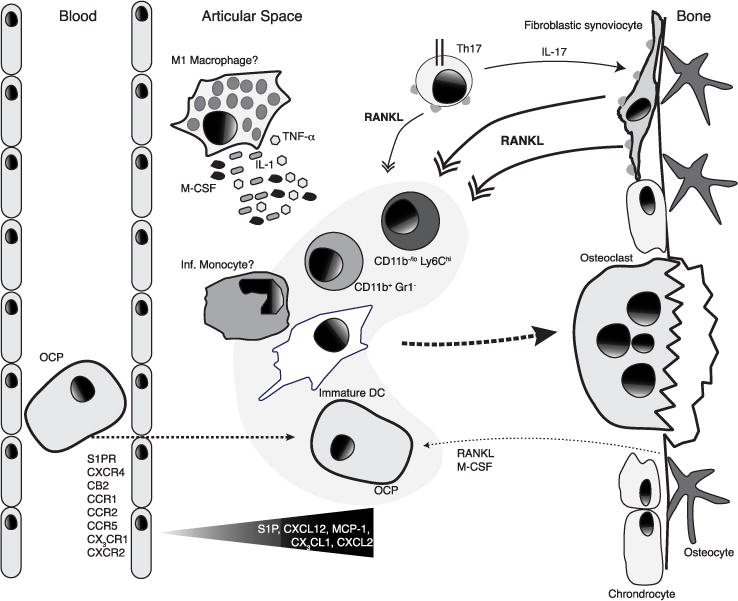
Trafficking of monocytic osteoclast precursors (OCP) into inflamed joints. Cells with osteoclastogenic potential include CD11b−/loLy6Chi, CD11b+GR-1−, and DCs. In RA, sinusoidal fibroblastic cells provide RANKL, which can be induced by IL-17 provided by Th17 cells. The cytokines TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6, which may be locally secreted by macrophages also promote osteoclast differentiation under inflammatory conditions. S1P receptor expression on OCPs possibly directs cells into the synovial tissue where S1P is upregulated during inflammation. CXCR4 also likely directs cells into the synovial tissue with fibroblasts, and possibly other cells, express high levels of CXCL12. Selective antagonism of CB2 inhibits the migration of monocytes into the synovium, indicating that 2-Ag levels may be present in synovial fluid. CXCR2, CX3CR1, CCR1, CCR2, and CCR5 are also implicated in inflammatory cell recruitment into the inflamed articular space.
