Figure 3.
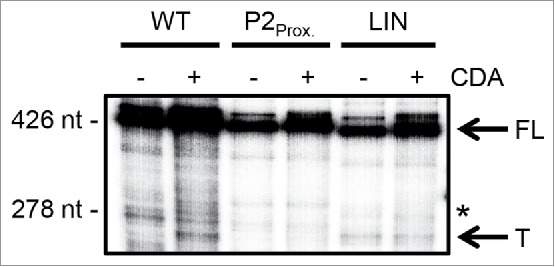
Cyclic di-AMP impact on rpfA transcript elongation by bacterial RNA polymerase. Wild-type (WT) and mutant (P2Prox., LIN) rpfA riboswitches were transcribed in vitro from an engineered B. subtilis lysC promoter using E. coli σ70-RNA polymerase. Reactions were supplemented with 0 µM (−) or 500 µM (+) cyclic di-AMP (CDA). Products were intrinsically labeled with 32P, size-fractionated on a denaturing urea-polyacrylamide gel and visualized by phosphorimaging. Image is representative of three biological replicates. The full-length gel image is presented in Fig. S5. FL, full-length transcripts; *, end of UTR(WT)-rpfA moiety (39 nt into the rpfA coding region); T, terminated transcripts.
