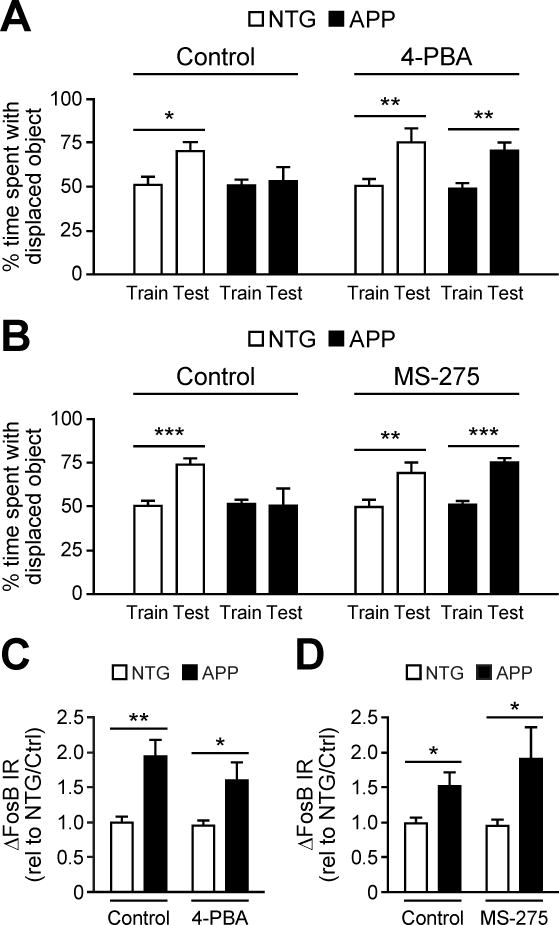
Figure 6. Acute HDAC inhibition improves hippocampus-dependent learning and memory in APP mice.
(A,B) APP mice exhibited increased time interacting with the displaced object during the test phase of the task when, prior to training, they were treated with either 4-PBA (n = 5–6/group) or MS-275 (n = 6/group) relative to treatment with vehicle (control). (C, D) Increased ΔFosB expression in APP vs. NTG mice is unaffected by 4-PBA (n = 5–6/group) or MS-275 (n = 7/group). Data in panels C–D were normalized to vehicle-treated NTG values (rel to NTG/Ctrl). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ns, non-significant. Error bars indicate SEM. See also Tables S3–S4.