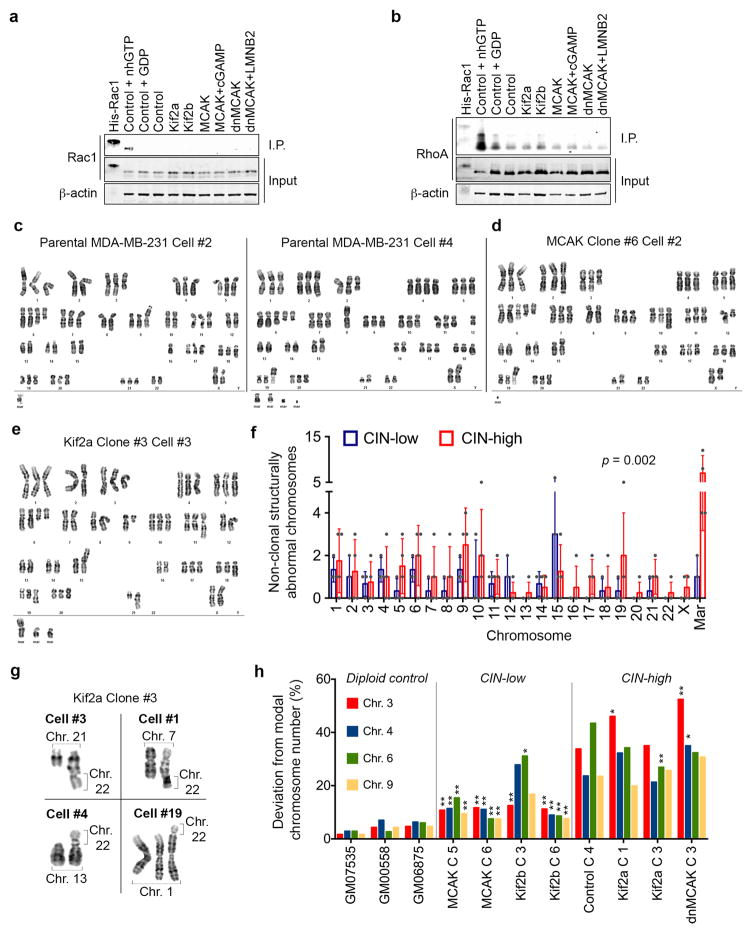
Extended Data Figure 2. Karyotype analysis of human tumor cells.
a–b, Immunoblots showing total Rac1 (a) or RhoA (b) levels as well as Rac1 or RhoA that were pulled-down using antibodies that were specific to the GTP-bound form of Rac1 (a) or RhoA (b). Positive and negative controls were total MDA-MB-231 cell lysates supplanted with non-hydrolysable GTP (nhGTP) or GDP, respectively. β-actin was used as a loading control, 2 independent experiments. c–e, Representative karyotypes (DAPI-banding) from parental MDA-MB-231 cells (c), or populations derived from single MCAK (d) or Kif2a (e) expressing cells that were allowed to divide for 30 days. f, The number of non-clonal (present in <25% of the cells in a single clone) structurally abnormal chromosomes in CIN-low or CIN-high MDA-MB-231 cells. ‘Mar’ denotes chromosomes so structurally abnormal that precludes their unambiguous identification by conventional banding, bars represent mean ± SD, n = 140 cells from 7 clonal populations, significance tested using two-way ANOVA test. g, Examples taken from 4 distinct cells belonging to the same clonal population – derived from a single Kif2a-expressing cell – showing convergent translocations involving chromosome 22 with four other chromosomes. h, Deviation from modal chromosome number in single-cell-derived clones grown for 30 days. Four chromosomes were assayed for each clone using centromere-specific probes, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005 compared to control clone 4, two-sided c2-test, n = 300 cells per clone. Diploid controls were used to determine false positive rate of the centromeric probes.