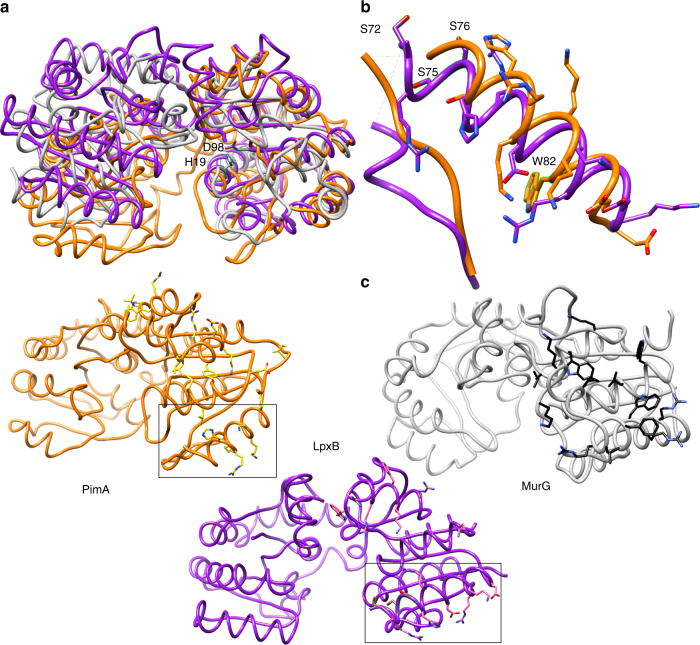
Fig. 5.
Membrane association. a Overlay of the N-terminal domains of LpxB7S (purple) with MurG (grey) (PDB: 1F0K)39 and PimA (orange) (PDB:2GEJ)48. The catalytic bases of LpxB and MurG, D98 and H19, respectively, are also shown. b Region of the LpxB-PimA membrane-binding face of particular interest. Deletion of the hydrophobic, flexible loop or mutation of basic residues in this helix to Ser inactivated PimA48, and mutation of hydrophobic residues in this loop and helix to Ser (visible residues highlighted) decreased LpxB activity. In addition, W82 in the PimA helix was shown to interact with negatively charged lipid membranes51. c Side-by-side comparison of the 3 proteins, showing residues that may be important for defining the membrane association surface. While the specific residues are not well conserved, they appear to form a similar hydrophobic and basic surface in all three enzymes. The regions of LpxB and PimA shown in b are boxed