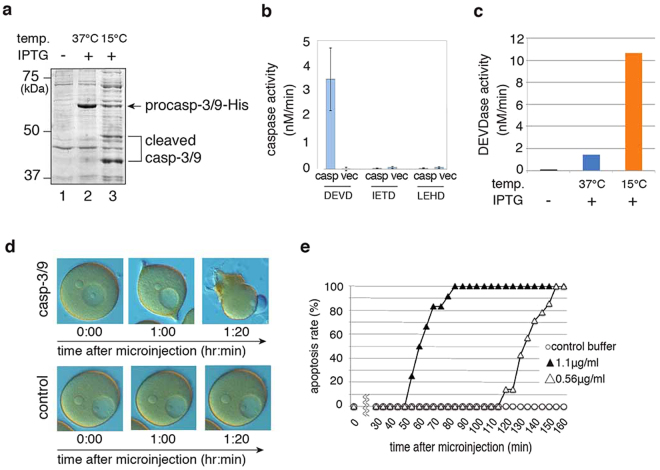
Figure 2.
Expression of, and proteolytic activity assay for, recombinant caspase-3/9. (a) SDS-PAGE analysis of recombinant procaspase-3/9-His6 expressed in E. coli with CBB gel staining. Lanes: (1) No IPTG induction; (2) Procaspase-3/9 with IPTG induction at 37 °C; (3) Cleaved caspase-3/9 with IPTG induction at 15 °C. Full gel is presented in Supplementary Fig. S10. (b) Specific proteolytic activity of recombinant caspase-3/9-His6. Cell lysate from E. coli either transformed with a vector encoding caspase-3/9-His6 (casp) or control vector (vec) were analyzed for caspase-3 (DEVD), -8 (IETD), and -9 (LEHD) catalytic activity using Ac-DEVD-MCA, Ac-IETD-MCA and Ac-LEHD-MCA, respectively. (c) DEVDase activity of recombinant caspase-3/9-His6 expressed at different temperatures. Cell lysate from E. coli without IPTG induction, with IPTG induction at 37 °C, and with IPTG induction at 15 °C were analyzed for DEVDase activity using Ac-DEVD-MCA. (d) Microinjection of caspase-3/9-His6 into oocytes. Purified caspase-3/9-His6 (1.1 µg/mL at a final concentration) or control buffer was microinjected into immature oocytes, and photographs were taken at the indicated times after microinjection. (e) The number of apoptotic eggs was counted after microinjection of purified caspase-3/9-His6 (closed triangle, 1.1 µg/mL; open triangle, 0.56 µg/mL at a final concentration) or control buffer (circle). The results are representative of four independent experiments.