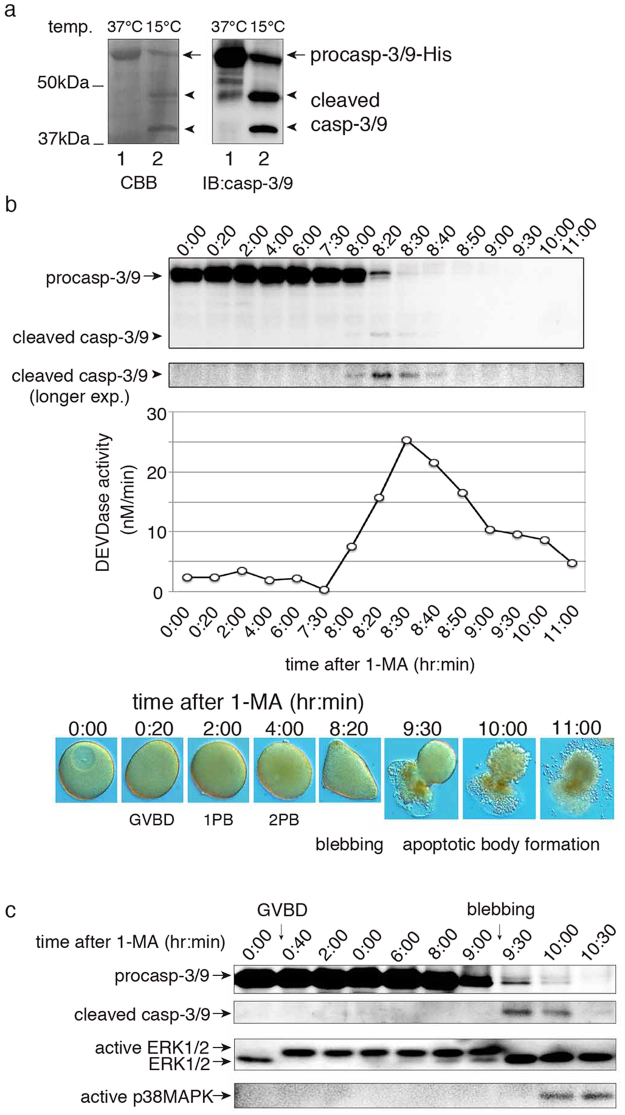
Figure 3.
Activation and cleavage of endogenous caspase-3/9 upon apoptosis in unfertilized eggs. (a) CBB gel staining and western blotting analysis of recombinant caspase-3/9-His6. Cell lysate of E. coli expressing recombinant caspase-3/9-His6 was subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by CBB gel staining (left panel), or analyzed by western blotting using the anti-caspase-3/9 antibody (right panel). Lanes: (1) with induction of IPTG at 37 °C; (2) at 15 °C. (b) Time course of endogenous caspase-3/9 activation after 1-MA treatment. Samples of oocytes were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting with the anti- caspase-3/9 antibody. Cleaved caspase-3/9 was visible after longer exposures. At the same time, the activity of endogenous caspase-3/9 was measured by the cleavage of Ac-DEVD-MCA. The morphological changes of the oocytes/eggs were observed with a light microscope equipped with Nomarski differential interference contrast optics; (0:00) immature oocyte; (0:20–4:00) mature eggs; (8:20) blebbing egg; (9:30–11:00) fragmented eggs. (c) Dynamics of caspase-3/9, ERK1/2 and p38MAPK during apoptosis. Samples were analyzed by western blotting with anti-caspase-3/9, anti-ERK1/2, and active p38MAPK-specific antibodies. Full gel and blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S10. The results are representative of three independent experiments.