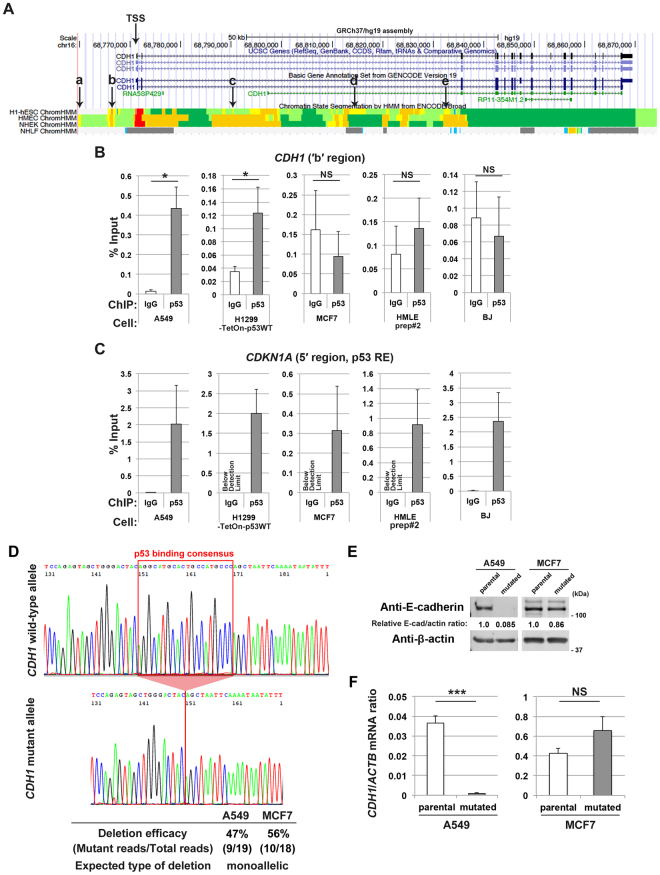
Figure 4.
p53 binds to the CDH1 locus to maintain its expression in EMT-prone cells. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of the ENCODE data at the CDH1 locus. The TSS and the p53 consensus binding motifs (a–e) across the CDH1 locus are indicated. (B,C) ChIP was performed using A549 cells, H1299-TetOn-p53WT cells cultured in the presence of doxycycline (0.5 µg/ml) for 48 h, MCF7 cells, HMLE prep#2 cells, or BJ cells with a normal rabbit IgG or anti-p53 antibody, followed by quantitative RT-PCR analysis with primers located at the ′b′ region of CDH1 (B) or at the p53 response element (RE) of CDKN1A (C). Data are means ± SD of 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05, NS, not significant versus corresponding IgG control (Student t-test). (D) Example chromatogram showing successful deletion of the p53-binding consensus. Efficiency of the targeted deletion in A549 cells or MCF7 cells determined by sequencing is indicated. (E) A549 cells or MCF7 cells with (mutated) or without (parental) deletion of the p53-binding motif were subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. Quantitative western blots of E-cadherin and β-actin (E-cad and actin, respectively) were performed with the infrared fluorescence imaging system on an Odyssey imager, and normalized E-cad/actin ratios are indicated. F, A549 cells or MCF7 cells as in (E) were subjected to quantitative RT-PCR analysis of CDH1 mRNA (normalized to ACTB mRNA). Data are means ± SD of 3 independent experiments. ***P < 0.0001; NS, not significant (Student t-test). Western blots were cropped for clarity; uncropped images are shown in Supplementary Figure S5.