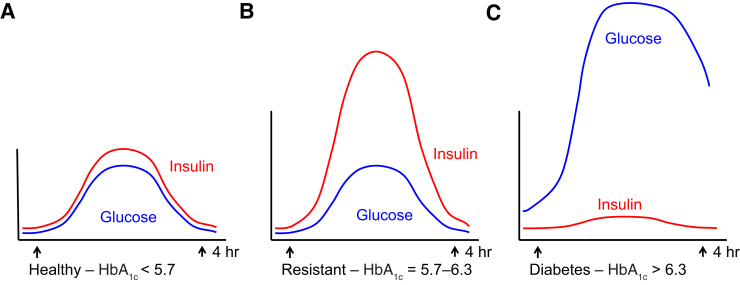
Figure 1.
Relative circulating insulin and glucose levels in a healthy individual (A), an insulin-resistant individual (B), and an individual with diabetes (C). Insulin resistance (prediabetes) occurs when the body demands increasingly greater amounts of insulin to deliver glucose to the muscle and other organs. When individuals with insulin resistance eat, insulin may increase to 5- to 10-fold higher than in individuals without insulin resistance. HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c.