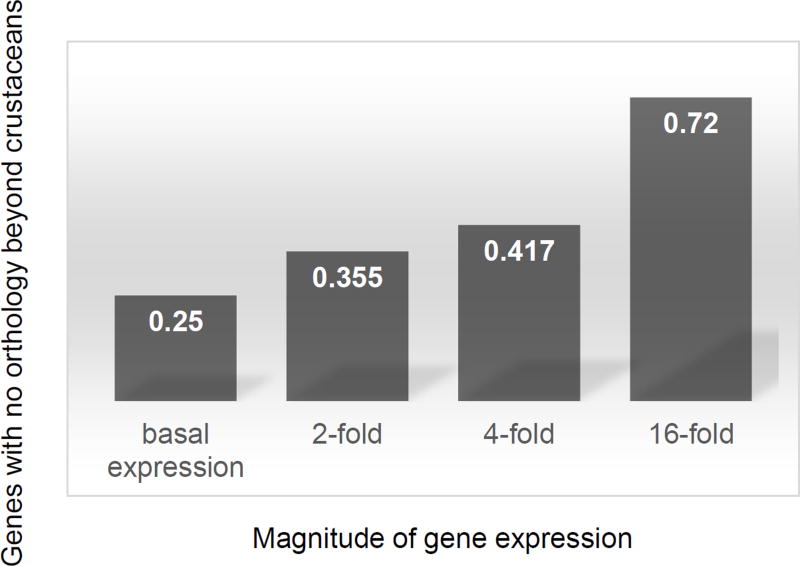
Figure 3. Conservation of genes responsive to environmental perturbations.
Genes responsive to environmental perturbations (N = 1,396 genes) are partitioned based on their magnitude of differential expression, ranging from basal expression (no differential expression under any perturbation) to 16-fold differential expression under at least one assayed environmental perturbation. For each category of differentially expressed genes the percentage of non-orthologous genes to other model species outside crustaceans is shown. The following model species were used for orthology searches: Danio rerio, Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila melanogaster, Mus musculus, and Homo sapiens. The two crustacean species Daphnia magna and Daphnia pulex were used in orthology searches to identify genes conserved within crustaceans. The percentage of genes with no orthology beyond crustaceans is indicated as percentage for each category of differentially expresses genes.