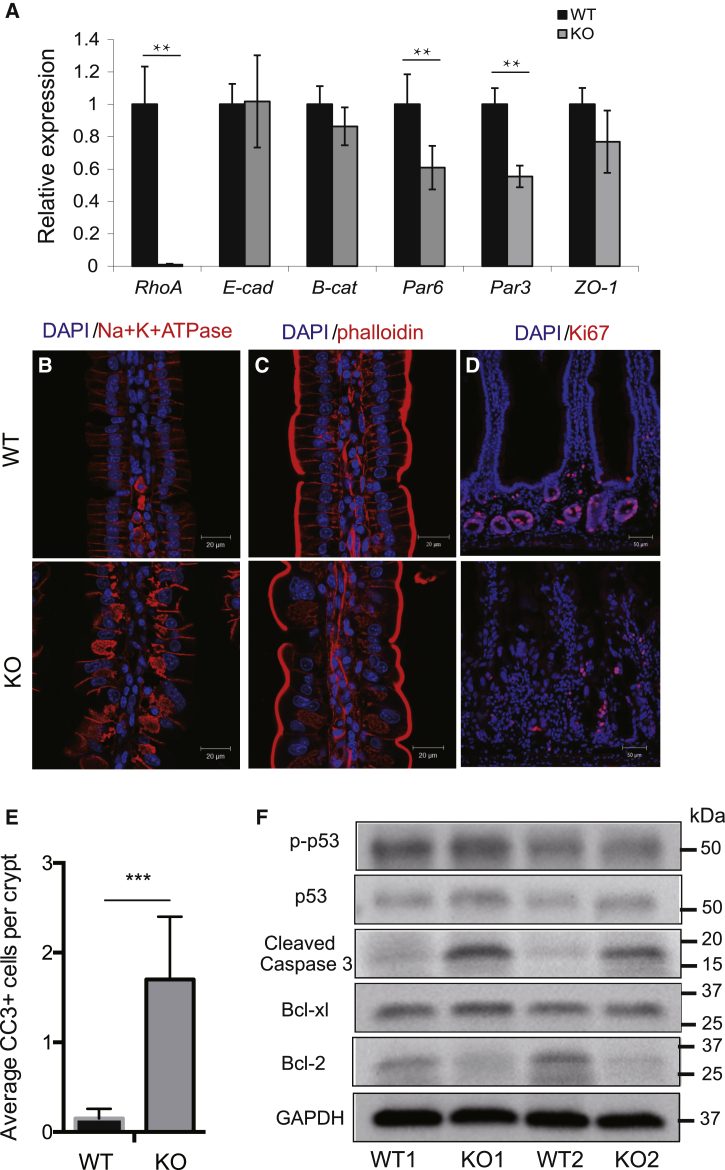
Figure 2.
Loss of RhoA Disrupts Epithelial Polarity and Adhesion, while Reducing Proliferation and Inducing Apoptosis in Small Intestine
(A) qRT-PCR analysis showing gene expression of cell junction and polarity markers in control WT and RhoA KO small intestine. Data are normalized to GAPDH expression; n = 3 mice per genotype. Error bars represent SD from three independent experiments.
(B–D) Representative immunofluorescence staining of Na+,K+-ATPase α (B), phalloidin (C), and Ki67 (D) in control WT and RhoA KO duodenum.
(E) Quantification of cleaved caspase-3-positive cells per crypt in control WT and RhoA KO duodenum. n = 4 mice for each genotype. Error bars represent SD from three independent experiments.
(F) Western blotting of apoptotic related proteins Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, p53, p-P53, and cleaved caspase-3 in duodenal crypts isolated from control and RhoA KO mice.
∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.