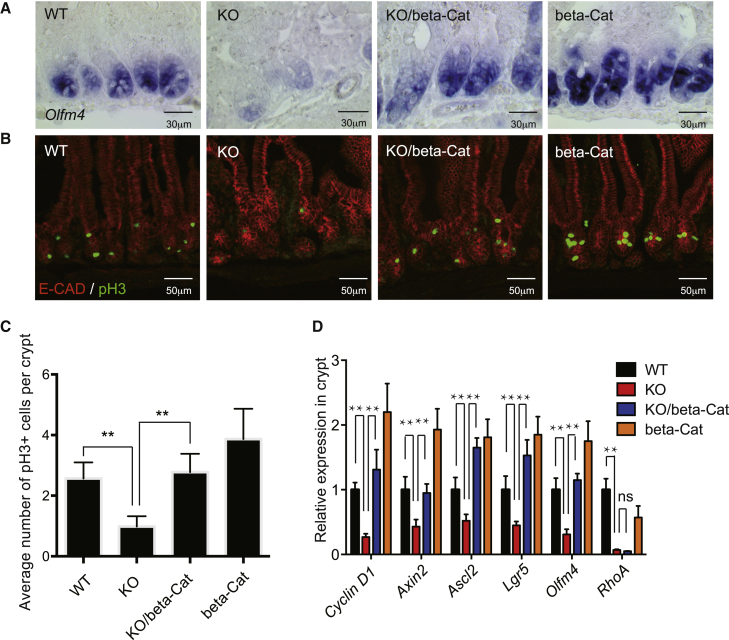
Figure 6.
Constitutively Active β-Catenin Overcomes the Loss of ISC Phenotype in RhoA KO Crypts
(A) In situ hybridization of Olfm4 RNA in control, RhoA KO, KO/β-catenin Catnblox(ex3) rescue, and β-catenin Catnblox(ex3) expressing duodenum.
(B) Representative immunofluorescence staining of phosphor-histone H3 in control WT, RhoA KO, KO/β-catenin Catnblox(ex3) rescue, and β-catenin Catnblox(ex3) expressing small intestine.
(C) Quantification of number of phosphor-histone H3-positive cells per crypt in control WT, RhoA KO, KO/β-catenin Catnblox(ex3) rescue, and β-catenin Catnblox(ex3) expressing small intestine. n = 3 mice for each genotype. Error bars represent SD from three independent experiments.
(D) qRT-PCR showing expression of ISCs markers and Wnt target genes in WT, RhoA KO, KO/β-catenin Catnblox(ex3) rescue, and β-catenin Catnblox(ex3) expressing crypts. Data are normalized to GAPDH expression; n = 3 mice for each genotype. Error bars represent SD from three independent experiments.
∗∗p < 0.01; ns, not significant.